Sketch a section of ticker tape for a trolley that travels at a steady velocity and then decelerates.

Important Questions on Accelerated Motion
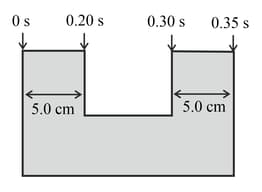
The figure drawn below shows the dimensions of an interrupt card, together with the times recorded as it passes through a light gate. Use these measurements to calculate the acceleration of the card.
Two adjacent five-dot sections of a ticker-tape measure and , respectively. The interval between dots is . Deduce the acceleration of the trolley that produced the tape.
A car is initially stationary. It has a constant acceleration of . Calculate the velocity of the car after .
A car is initially stationary. It has a constant acceleration of . Calculate the distance travelled by the car at the end of .
A car is initially stationary. It has a constant acceleration of . Calculate the time taken by the car to reach a velocity of .
A car is moving at . The driver makes it accelerate at for a distance of . What is the final velocity of the car?
Trials on the surface of a new road show that, when a car skids to a halt, its acceleration is . Estimate the skid-to-stop distance of a car travelling at a speed limit of (approximately or ).
At the scene of an accident on a country road, police find skid marks stretching for . Tests on the road surface show that a skidding car decelerates at . Was the car that skidded exceeding the speed limit of on this road?
