Sketch the displacement-time graphs from the information given. In each case consider forwards to be the positive direction and the traffic lights to be the point from which displacement is measured. Remember to include the values for time and displacement at any points where the motion changes.
A motorbike passes the traffic lights at a constant speed of After it starts to slow at a constant rate of until it comes to rest.

Important Questions on Velocity and Acceleration
Sketch the displacement-time graphs from the information given. In each case consider forwards to be the positive direction and the traffic lights to be the point from which displacement is measured. Remember to include the values for time and displacement at any points where the motion changes.
A truck is moving at a constant speed of and is approaching the traffic lights away. When it is away it accelerates at a constant rate of to get past the lights before they change colour.
Sketch the displacement-time graphs from the information given. In each case consider forwards to be the positive direction and the traffic lights to be the point from which displacement is measured. Remember to include the values for time and displacement at any points where the motion changes.
A scooter accelerates from rest before the traffic lights at a constant rate of until it reaches It then travels at this speed until it reaches a point beyond the traffic lights. At that point the scooter starts to slow at a constant rate of until it stops.
The sketch shows a displacement-time graph of the position of a train passing a station. The displacement is measured from the entrance of the station to the front of the train. Find the equation of the displacement-time graph and hence the time at which the front of the train reaches the entrance of the station.
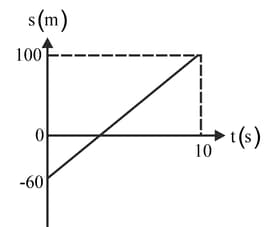
The sketch shows a displacement-time graph of a car slowing down with constant acceleration before coming to rest at a set of traffic lights.
The equation of the displacement-time graph can be written in the form Using the two points marked and the fact that the car is stationary at find and
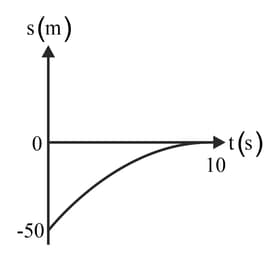
The sketch shows a displacement-time graph of a car slowing down with constant acceleration before coming to rest at a set of traffic lights.
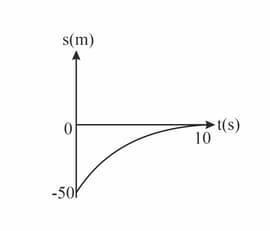
By comparison with the equation Find the initial speed and acceleration of the car.
