Starting from rest, a body slides down a inclined plane in twice the time it takes to slide down the same distance in the absence of friction. The coefficient of friction between the body and the inclined plane is

Important Questions on Friction
A wooden block of mass resting on a rough horizontal table (coefficient of friction ) is pulled by a force , as shown in the figure. The acceleration of the block moving horizontally is:
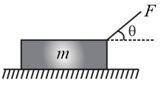
A block of mass is resting on a rough horizontal surface for which the coefficient of friction is When a pulling force is applied, the acceleration of the block will be:
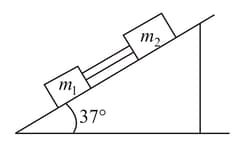
Two blocks, and , are connected by a weightless rod on a plane having an inclination of . If the coefficient of dynamic friction of and , with the inclined plane is , then the common acceleration of the two blocks and the tension in the rod, respectively, are:
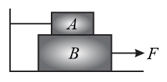
A force is applied to block as shown in the figure. The force is applied at seconds when the system was at rest and the string is just straight without tension. Which of the following graphs gives the frictional force between block and the horizontal surface as a function of time
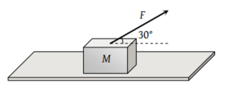
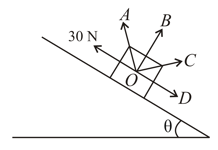
A body of mass lies on a rough inclined plane of inclination with the horizontal. When a force of is applied on the block parallel on an upward the plane, the total reaction by the plane on the block is nearly along,
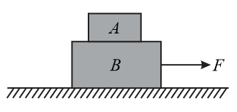
Block of mass and block of mass are resting on a horizontal surface, as shown in the figure. There is no friction between the block and the horizontal surface. The coefficient of friction between the blocks is If the value of , then the maximum horizontal force that can be applied on the block without any relative motion between and is:
Two blocks and plane surface as shown in the figure. The mass of block is and that of block is . Block is tied to a stand and block is pulled by a force If the coefficient of friction between the surfaces of and is and the coefficient of friction between and the plane is then for the motion of the minimum value of will be: