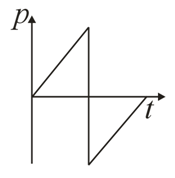
Starting from rest, a car moves with a constant acceleration, and comes to a momentary stop with the same constant deceleration. Subsequently, it reverses its motion and returns to its original position in a similar manner. Which one of the following graphs of momentum versus time best describes the motion of the car?
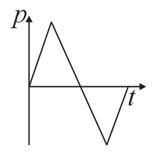
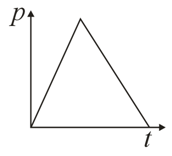
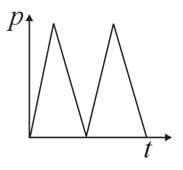
Important Questions on Centre of Mass, Momentum and Collisions
(i) second, (ii) seconds, respectively.
Choose the correct option out of the following :
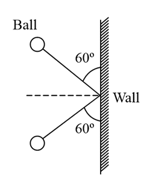
A ball of mass , moving with a speed of , strikes a wall at an angle (as shown in figure). The ball rebounds at the same speed and remains in contact with the wall for ; the force exerted by the ball on the wall is:
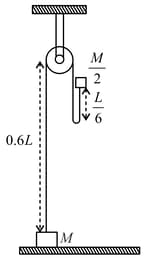
A block of mass at rest on the floor is attached to a ball of mass via a light inextensible string of length which passes over a light small frictionless pulley. The pulley is at a height of from the floor. The ball is raised to a height of and released (see figure). The speed of the block at the instant the string gets taut (not slack) will be
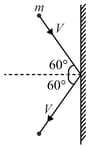
A rigid ball of mass, strikes a rigid wall at and gets reflected without any loss of speed as shown in the figure below. The value of impulse imparted by the wall on the ball will be
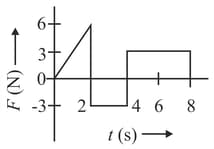
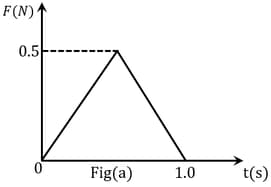
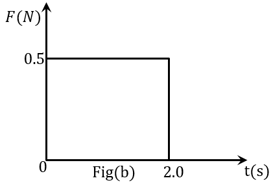
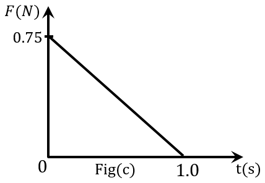
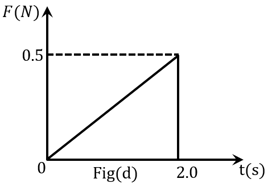
Figures (a), (b), (c) and (d) show variation of force with time.
The impulse is highest in figure.
A block of mass rests on another block of mass and is tied to a wall as shown in the figure. The coefficient of friction between and is and that between and ground is . The minimum force required to move the block is

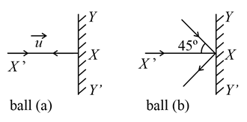
Two billiard balls of equal mass strike a rigid wall with same speed of (as shown) but at different angles. If the balls get reflected with the same speed, then the ratio of the magnitude of impulses imparted to ball and ball by the wall along direction is:
The correct dimensional formula for impulse is given by
A time varying force acts on a ball of mass for . The force versus time curve is shown below. If the initial speed of the ball is , then the speed of ball after is
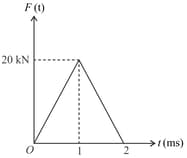
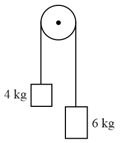
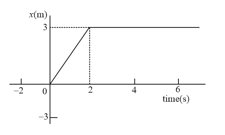
Figure represents the position-time graph of a body of mass . Impulse imparted to the body at is
The force acting on a particle of mass is indicated by the force-time graph shown below. The change in momentum of the particle over the time interval from zero to is: