State one assumption made in deriving the formula for refraction at a spherical interface.

Important Questions on Refraction of Light at Spherical Surfaces : Lenses
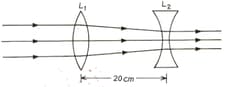
A thin convex lens of focal length and a thin concave lens of focal length are kept co-axially apart as shown in figure below. When a narrow and parallel beam of light is incident on the convex lens, beam emerging from the concave lens is also a parallel beam. Find .
Write down the lens maker’s formula, using standard symbols.
How does focal length of a convex lens change with increase in wavelength of incident light?
Under what condition is the first focal length of a lens not equal to its second focal length?
The image of an object, placed at a distance of from a lens, is formed at a distance of on the other side of the lens. If the object is placed at a distance of from the lens, find the position of the image.
A convex lens forms a virtual image of an object. Where is the object? Answer in terms of focal length.
Where should an object be placed in order to form an image of the same size by a convex lens? Can it happen in case of a concave lens also?
