Statement = for an ideal gas
Explanation for an ideal gas.
Important Questions on Thermodynamics
The molar heat capacity for an ideal gas at constant pressure is . The change in internal energy is upon heating it from to . The number of moles of the gas at constant volume is____
(Given: )
The specific heat of a certain substance is . Assuming ideal solution behavior, the energy required (in ) to heat of molal of its aqueous solution from to is closest to :
[Given: molar mass of the substance ; specific heat of water ]
fish swimming in water body when taken out from the water body is covered with a film of water of weight . When it is subjected to cooking at , then the internal energy for vaporization in is integer]
[Assume steam to be an ideal gas. Given for water at and bar is ]
The quantity of heat (in ) required to raise the temperature of of ethanol from to the boiling point and then change the liquid to vapor at that temperature is closest to [Given, boiling point of ethanol . Specific heat capacity of liquid ethanol . Latent heat of vaporisation of ethanol ]
The combination of plots which does not represent isothermal expansion of an ideal gas is
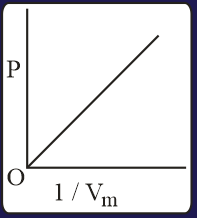
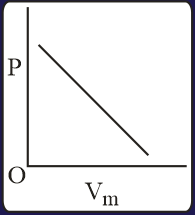
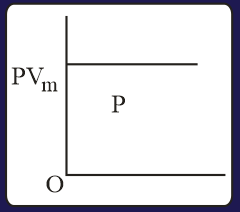
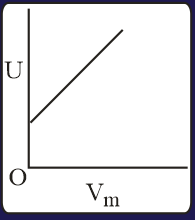
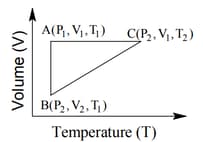
The correct option(s) is (are)
of is mixed with of The molar heat of neutralization of this reaction is The increase in temperature in of the system on mixing is The value of is (Nearest integer)
[Given: Specific heat of water
Density of water]
(Assume no volume change on mixing)
[Heat of fusion of ice ; Specific heat of water ]

