Suggest how the below idea might decrease the chances of developing an antibiotic-resistant strain of bacteria:
Using two or more antibiotics together to treat a bacterial infection.

Important Questions on Infectious Disease
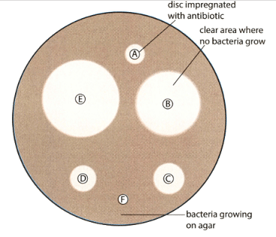
The below figure shows the results of an antibiotic sensitivity test carried out on a pathogenic strain of the human gut bacterium Escherichia coli 0157. Bacteria are collected from faeces, food or water, and grown on an agar medium. Various antibiotics are absorbed onto discs of filter paper and placed on the agar plate. The plate is incubated, and the diameters of the inhibition zones where no bacteria are growing are measured.
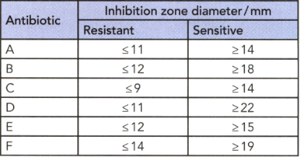
The table below shows the inhibition zone diameters for the antibiotics included in the figure.
If the diameter of the inhibition zone for an antibiotic is equal to or less than () the figure given in the first column of the table, the bacteria are resistant to it. If the diameter is equal to or greater than () the figure in the right-hand column, the bacteria are sensitive, and the antibiotic may be chosen for treatment. Which of the antibiotics in figure and table would be chosen to treat the patient with the pathogenic strain of E. coli 0157? Explain your answer.
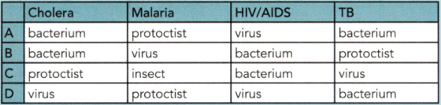
Cholera, malaria, HIV/AIDS and TB are infectious diseases. Which row shows the type of organism that causes each of these diseases? (Answer the alphabet only)
An antibiotic sensitivity test was carried out on bacteria isolated from a patient with a blood disease. Four antibiotics were tested, A, B, C and D. The results are shown in the diagram.
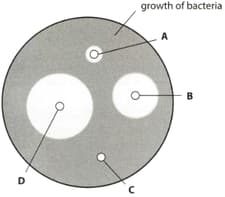
Which antibiotic is likely to be the most effective in treating blood disease?
