MEDIUM
10th CBSE
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
Sulphur dioxide turns acidified potassium dichromate solution
(a)black
(b)blue
(c)red
(d)green
50% studentsanswered this correctly

Important Questions on Practical Chemistry
MEDIUM
10th CBSE
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
10th CBSE
IMPORTANT
EASY
10th CBSE
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
10th CBSE
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
10th CBSE
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
10th CBSE
IMPORTANT
A student added acetic acid to test tubes I, II, III and IV containing the labelled substances and then brought a burning splinter near the mouth of each test tube.
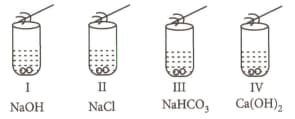
The splinter would be extinguished when brought near the mouth of test tube
MEDIUM
10th CBSE
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
10th CBSE
IMPORTANT
