The angular momentum of a particle relative to a certain point varies with time as , where and are constant vectors, with . Find the force moment relative to the point acting on the particle when the angle between the vectors and equals .

Important Questions on Rotational Mechanics
A plank of mass , with a uniform sphere of mass placed on it, rests on a smooth horizontal plane. A constant horizontal force is applied to the plank. With what accelerations will the plank and the centre of the sphere move, provide there is no sliding between the plank and the sphere?
In the arrangement shown in the figure, weight possesses mass , a pulley possesses mass . Also known are the moment of inertia of the pulley relative to its axis and the radii of the pulley are and , respectively. Consider the mass of the threads is negligible. Find the acceleration of weight after the system is set free. (Assume no slipping takes place anywhere and axis of cylinder remains horizontal)
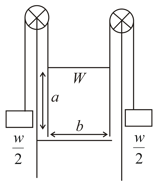
A window (of weight ) is supported by two strings passing over two smooth pulleys in the frame of the window in which window just fits in, the other ends of the string being attached to weights each equal to half the weight of the window. One thread breaks and the window moves down. Find acceleration of the window if is the coefficient of friction, and is the height and the breadth of the window.
A diameter pipe of mass rests on a plate. The pipe and plate are initially at rest when a force of magnitude is applied for . Knowing that between the plate and both the pipe and the floor, determine;
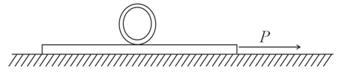
(a) whether the pipe slides with respect to the plate.
(b) the resulting velocities of the pipe and of the plate.
A uniform disc of mass and radius is projected horizontally with velocity on a rough horizontal floor, so that it starts off with a purely sliding motion at . After seconds, it acquires a purely rolling motion as shown in the figure.
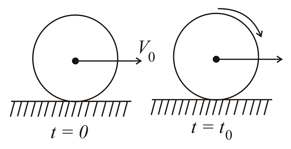
(a) Calculate the velocity of the centre of mass of the disc at .
(b) Assuming the coefficient of friction to be , calculate . Also calculate the work done by the frictional force as a function of time and the total work done by it over a time much longer than .
Two uniform thin rods of length each and of masses , respectively, are rigidly joined, end to end. The combination is pivoted at the lighter end as shown in figure such that it can freely rotate about the point in a vertical plane. A small object of mass moving horizontally hits the lower end of the combination and sticks to it. What should be the velocity of the object so that the system could just be raised to the horizontal position?
A bar of mass is held as shown between disks, each of mass . Determine the acceleration of the bar immediately after it has been released from rest, knowing that the normal forces exerted on the disks are sufficient to prevent any slipping and assuming that; In (i) case, the discs are attached to the fixed support on wall. In (ii) case, the discs are attached to the bar.
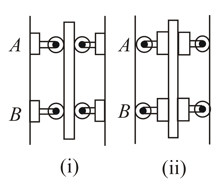
(a) .
(b) the mass of of the disks is negligible.
(c) the mass of of the bar is negligible.
