EASY
Earn 100
The average kinetic energy of gas molecules does not depend upon temperature.
(a)True
(b)False
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Kinetic Theory
MEDIUM
Boltzmann Constant
Avogadro number
Radius of Earth:
Gravitational acceleration on Earth
MEDIUM
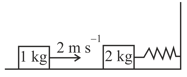
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
EASY
HARD
EASY
HARD

