HARD
Earn 100
The boiling point of an aqueous solution of a non-volatile solute is . What is the freezing point of an aqueous solution obtained by diluting the above solution with an equal volume of water? The values of and for water are and respectively.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
58.33% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Solutions
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
HARD
The plot given below shows curves (where, is the pressure and is the temperature) for two solvents and and isomolal solutions of in these solvents. completely dissociates in both the solvents.
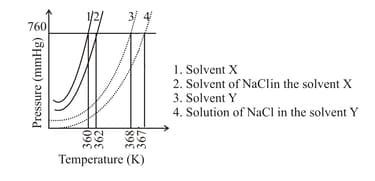
On the addition of equal number of moles of a non-volatile solute in equal amount (in ) of these solvents, the elevation of boiling point of solvent is three times that of solvent . The solute is known to undergo dimerization in these solvents. If the degree of dimerization is in the solvent , the degree of dimerization in the solvent is _______.
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
HARD
EASY
[Assume ionisation of the complex and coordination number of as and that all molecules are present inside the coordination sphere]
MEDIUM
for water is
EASY
MEDIUM

