The circuit shown in Figure produces a decreasing output voltage when the light intensity increases. How can the circuit be altered to produce an increasing output voltage as the light intensity increases?
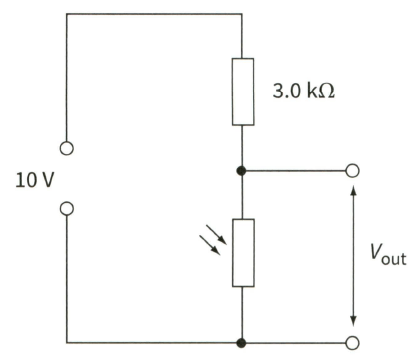
An LDR used as a sensor.


Important Questions on Practical Circuits
Design a circuit using the thermistor in Figure that uses a cell of and produces an output voltage of at . Explain whether the voltage output of your circuit increases or decreases as the temperature rises.
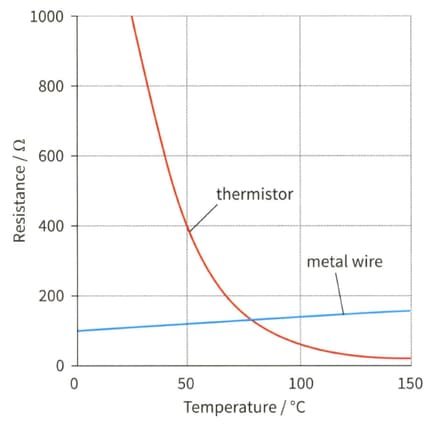
Variation of resistance with temperature.
To make a potentiometer, a driver cell of e.m.f. is connected across a length of resistance wire.
(a) What is the potential difference across each length of the wire? What length of wire has a p.d. of across it?
To make a potentiometer, a driver cell of e.m.f. is connected across a length of resistance wire.
(b) A cell of unknown e.m.f. is connected to the potentiometer and the balance point is found at a distance of from the end of the wire to which the galvanometer is connected. Estimate the value of . Explain why this can only be an estimate.
To make a potentiometer, a driver cell of e.m.f. is connected across a length of resistance wire.
(c) A standard cell of e.m.f. gives a balance length of Use this value to obtain a more accurate value for .
A resistor of resistance and a second resistor of resistance are connected in parallel across a battery of e.m.f. and internal resistance . What is the current in the battery?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
This diagram shows a potential divider.
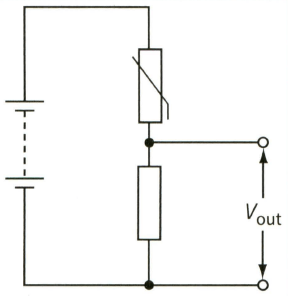
What happens when the temperature decreases?
(A) The resistance of the thermistor decreases and decreases.
(B) The resistance of the thermistor decreases and increases.
(C) The resistance of the thermistor increases and decreases.
(D) The resistance of the thermistor increases and increases.
