EASY
Earn 100
The coil of a moving coil galvanometer has an effective area of It is suspended in a magnetic field of If the deflection in the galvanometer coil is when a current of is passed through it, then
(a)Torsional constant is
(b)Current sensitivity is
(c)Torsional constant is
(d)Current sensitivity is
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Current Electricity
MEDIUM
A galvanometer of resistance requires current for full scale deflection. Now a resistance of is connected to convert it into an ammeter. The minimum current required to obtain full scale deflection is
MEDIUM
The range of an ammeter of resistance can be increased from to by connecting
EASY
An ammeter of resistance can measure currents upto . The value of shunt resistance to measure current upto is
EASY
This question has and . Of the four choices given after the Statements, choose the one that best describes the two Statements.
Higher the range, greater is the resistance of ammeter.
To increase the range of ammeter, additional shunt needs to be used across it.
EASY
A circuit contains an ammeter, a battery of 30 v and a resistance 40.8 ohm all connected in series. If the ammeter has coil of resistance 480 ohm and a shunt of 20 ohm, the reading in the ammeter will be:
EASY
A galvanometer gets full scale deflection when a current of pass through the coil. When it is converted to a ammeter, the shunt resistance is
EASY
The deflection in galvanometer falls to $\left(\frac{1}{4}\right)^{\operatorname{th}}$ when it is shunted by . If additional shunt of is connected to earlier shunt, the deflection in galvanometer falls to
EASY
An ammeter reads up to . Its internal resistance is . To increase the range to the value of the required shunt is
MEDIUM
A resistance is connected to a battery of . A galvanometer of resistance is to be used as an ammeter to measure current through the resistance, for this a resistance is connected to the galvanometer. Which of the following connections should be employed if the measured current is with in of the current without the ammeter in the circuit?
HARD
A moving coil galvanometer, having a resistance produces full scale deflection when a current flows through it. This galvanometer can be converted into (i) an ammeter of range 0 to by connecting a shunt resistance to it and (ii) into a voltmeter of range 0 to by connecting a series resistance to it. Then,
MEDIUM
The deflection in the galvanometer falls to when resistance is connected in parallel with it. What will be the deflection if an additional resistance of is connected in parallel with the above shunted galvanometer?
EASY
A galvanometer with its coil resistance requires a current of for its full deflection. In order to construct an ammeter to read up to a current of the approximate value of the shunt resistance should be:
MEDIUM
How do you convert a moving coil galvanometer into an ammeter?
EASY
A galvanometer having a resistance of is shunted by a wire of resistance If the total current is the part of it passing through the shunt will be
MEDIUM
Distinguish between ammeter and voltmeter.
MEDIUM
Consider a galvanometer shunted with resistance and of current passes through it. What is the resistance of the given galvanometer?
EASY
A galvanometer has a coil of resistance and requires for full-scale deflection. The shunt resistance needed to convert the galvanometer into an ammeter of the range is
MEDIUM
In an ammeter of main current passes through the galvanometer. If resistance of galvanometer is the resistance of ammeter will be:
MEDIUM
A galvanometer has a 50 division scale. Battery has no internal resistance. It is found that there is deflection of 40 divisions when Deflection becomes 20 divisions when resistance taken from resistance box is 4900 Ω. Then we can conclude :
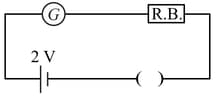
Note: This question is awarded as the bonus. Now the question is corrected.
HARD
In a circuit for finding the resistance of a galvanometer by half deflection method, a battery and a high resistance of are used. The figure of merit of the galvanometer is . In the absence of shunt resistance, the galvanometer produces a deflection of divisions when current flows in the circuit. The value of the shunt resistance that can cause the deflection of , is closest to:

