EASY
Earn 100
The collision between the molecules of an ideal gas is perfectly elastic.
(a)True
(b)False
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Kinetic Theory of Gases and Radiation
MEDIUM
Two moles of an ideal gas, with , are mixed with three moles of another ideal gas . The value of for the mixture is
EASY
Which of the following curves represent the variation of coefficient of volume expansion of an ideal gas at constant pressure?
EASY
If the water is converted into ice, and its entropy is changed by then
HARD
State any ‘four’ assumptions of the kinetic theory of gases.
HARD
Particle of mass moving along the -axis with velocity collides elastically with another particle at rest having mass . If both the particles move along the -axis after the collision, the change in the wavelength of the particle , in terms of its de-Broglie wavelength before the collision is:
EASY
Some smoke is trapped in a small glass container and is viewed through a microscope. A number of very small smoke particles are seen in continuous random motion as a result of their bombardment by air molecules. If the mass of the smoke particle is about times higher than that of an air molecule the average speed of a smoke particle is
MEDIUM
A mixture of hydrogen and oxygen has volume temperature pressure and mass The ratio of masses of oxygen to hydrogen will be:
EASY
If pressure and temperature of an ideal gas are doubled and volume is halved, the number of molecules of gas
EASY
An ideal gas equation can be written as, where and are respectively,
EASY
According to the assumptions made in the kinetic theory of gases, when two molecules of a gas collide with each other then
MEDIUM
One mole of an ideal gas passes through a process where pressure and volume obey the relation . Here and are constants. Calculate the change in the temperature of the gas if its volume changes from to .
MEDIUM
A spring - block system is resting on a frictionless floor as shown in the figure. The spring constant is and the mass of the block is . Ignore the mass of the spring. Initially the spring is in an unstretched condition. Another block of mass moving with a speed of collides elastically with the first block. The collision is such that the block does not hit the wall. The distance, in metres, between the two blocks when the spring returns to its unstretched position for the first time after the collision is _________.
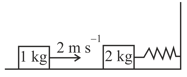
MEDIUM
As per Gay-Lussac's law, the volumes of solids and liquids are considered to be _____.
EASY
Name the three thermodynamic parameters of the gas.
EASY
The volume of a gas varied linearly with absolute temperature if its pressure is held constant. Suppose the gas does not liquify even at very low temperatures, at what temperature the volume of the gas will be ideally zero?
HARD
Let us assume that air is under standard conditions close to the Earth's surface. Presuming that the temperature and the molar mass of air are independent of height, find the air pressure at a height over the surface and in a mine, at the depth of below the surface.
EASY
Define Gay-Lussac’s law.
EASY
What is the value of universal gas constant ?
HARD
A horizontal cylinder, closed from one end, is rotated with a constant angular velocity about a vertical axis passing through the open end of the cylinder. The outside air pressure is equal to , the temperature is and the molar mass of air is . Find the air pressure as a function of the distance from the rotation axis. The molar mass is assumed to be independent of .
HARD
A vessel filled with air under pressure , contains a soap bubble of diameter . The air pressure, having been reduced isothermally, -fold, the bubble diameter increased -fold. Find the surface tension of the soap water solution.

