The diagram given below represents an experimental set-up to demonstrate a certain process. Study the same and answer the questions that follow :
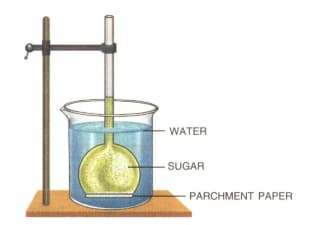
(a) Name the process.
(b) Define the above-named process.
(c) What would you observe in the experimental set-up after an hour or so?
(d) What control experiment can be set up for comparison?
(e) Keeping in mind the root-hair, cell and its surroundings, name the parts that correspond to (1) concentrated sugar solution (2) parchment paper and (3) water in the beaker.
(f) Name any other material that can be used instead of parchment paper in the above experiment
(g) Mention two advantages of the process to the plants


Important Questions on Absorption by Roots - The Processes Involved
The diagram below represents a layer of epidermal cells showing a fully grown root hair. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow:
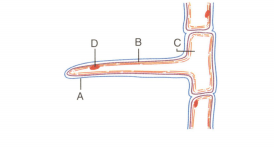
(a) Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D.
(b) The root hair cell is in a turgid state. Name and explain the process that caused this state.
(c) Mention one distinct difference between the parts labelled A and B.
(d) Draw a diagram of the above root hair cell as it would appear when a concentrated solution of fertilizers is added near it.
Study the diagram given below and answer the questions that follow :
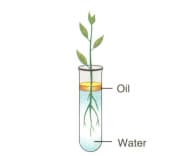
(a) Name the process being studied in the above experiment.
(b) Explain the process mentioned in (a) above
(c) Why is oil placed over water?
(d) What do we observe with regard to the level of water when this set up is placed in (1) bright sunlight (2) humid conditions (3) windy day?
(e) Mention any three adaptations found in the roots of the plant which enable them to carry out the process mentioned in (a).
Three cylinders of potato were carefully dried on a blotting paper and weighed. Each piece weighed 3 grams. Each one was placed in the beaker as shown below:
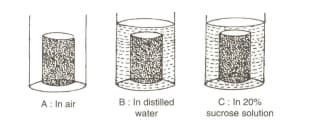
Answer the following questions:
(a) After 48 hours, which potato cylinder would be the heaviest?
(b) The movement of which substance is mainly responsible for the weight change in the potato cylinders?
(c) Name and define the process which is responsible for the movement of substance mentioned in answer (b).
(d) Write specific names of the processes which occur in beakers B and C. [kinds of processes defined in answer (c)].
(e) Would there be any difference in the weight of the potato cylinder in beaker A after 48 hours? Give reason.
The figure given below is a diagrammatic representation of a part of the cross-section of the root in the root hair zone. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow :
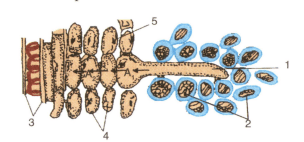
(a) Name the parts indicated by guidelines 1 to 5.
(b) Is the root hair cell unicellular or multicellular ?
(c) Explain what would happen to the root hair cell if some fertilizer is added to the soil close to it.
(d) Name the process responsible for the entry of water molecules from the soil into A1 and then into A2•
(e) What pressure is responsible for the movement of water in the direction indicated by arrows ?
(f) How is this pressure set up ?
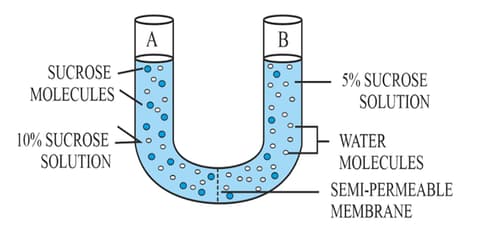
Study the experimental set-up in the figure and then answer the questions that follow:
(a) What phenomenon is being studied by this set-up?
(b) Explain the phenomenon mentioned in (a) above
(c) What is meant by 'semipermeable membrane'?
(d) What will you observe in the set-up after about half an hour? Give a reason for your answer.
A candidate in order to study the process of osmosis has taken 3 potato cubes and put them in 3 different beakers containing 3 different solutions. After 24 hours, in the first beaker the potato cube increased in size, in the second beaker the potato cube decreased in size and in the third beaker there was no change in the size of the potato cube. The following diagram shows the result of the same experiment:
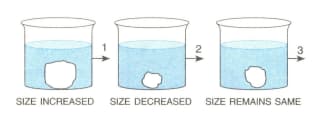
(a) Give the technical terms of the solutions used in beakers, 1, 2 and 3.
(b) In beaker 3, the size of the potato cube remains the same. Explain the reason in brief
(c) Write the specific feature of the cell sap of root hairs which helps in absorption of water.
(d) What is osmosis?
(e) How does a cell wall and a cell membrane differ in their permeability?
