The diagram shows a cylinder in vacuums, which has a movable, frictionless piston at the top. An ideal gas is kept in the cylinder. The piston is at a distance of from the bottom of the cylinder and the volume of the cylinder . The weight on the top of the cylinder has a mass of . The temperature of the gas is .
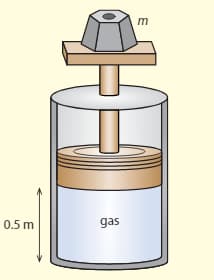
b. Determine how many molecules there are in the gas.


Important Questions on Thermal Physics
The diagram shows a cylinder in vacuums, which has a movable, frictionless piston at the top. An ideal gas is kept in the cylinder. The piston is at a distance of from the bottom of the cylinder and the volume of the cylinder . The weight on the top of the cylinder has a mass of . The temperature of the gas is .
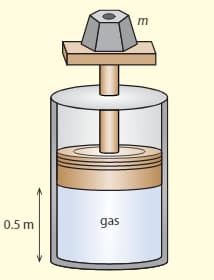
c. The temperature is increased to . Calculate the new volume of the gas.
A flask has a volume of and contains air at a temperature of and a pressure of .
(a) Calculate the number of moles of air in the flask.
A flask has a volume of and contains air at a temperature of and a pressure of .
(b) Determine the number of molecules in the flask.
A flask has a volume of and contains air at a temperature of and a pressure of .
(c) Estimate the mass of air in the flask. You may take the molar mass of air to be .
The molar mass of helium is .
a. Calculate the volume of of helium at standard temperature and pressure (STP) i.e., at
The molar mass of helium is . Calculate the volume of of helium at standard temperature and pressure (STP) i.e., at
b. Determine the density of helium at STP.
