EASY
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
The diagram shows the maximum kinetic energy $E$ of the emitted photoelectrons as the frequency $f$ of the incident radiation on a sodium plate is varied.
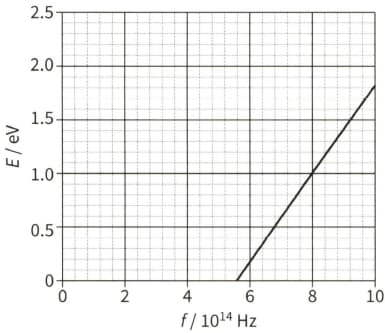
Explain why there are no photoelectrons emitted when the frequency of the incident light is less than $5.6 \times 10^{14} \mathrm{~Hz} .$


Important Questions on Quantum Physics
EASY
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
The diagram shows the maximum kinetic energy $E$ of the emitted photoelectrons as the frequency $f$ of the incident radiation on a sodium plate is varied.
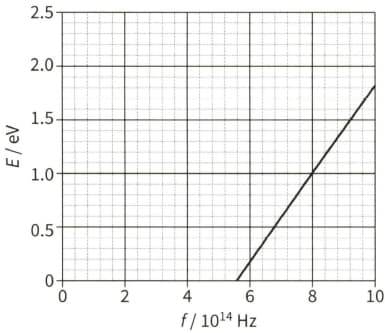
EASY
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
The diagram shows the maximum kinetic energy $E$ of the emitted photoelectrons as the frequency $f$ of the incident radiation on a sodium plate is varied.
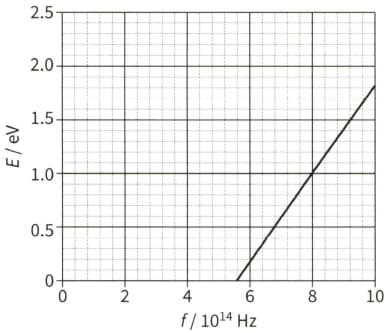
EASY
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
State what is meant by the de Broglie wavelength of an electron.
EASY
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
The diagram shows the principles of an electron tube used to demonstrate electron diffraction.
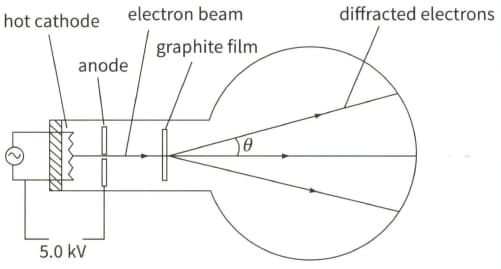
Calculate the kinetic energy $E$ (in joules) of the electrons incident on the graphite film.
MEDIUM
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
The diagram shows the principles of an electron tube used to demonstrate electron diffraction.
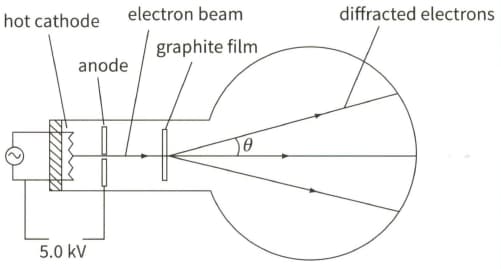
Show that the momentum of an electron is equal to $\sqrt{2 E m_{e}}$ where $m_{\mathrm{e}}$ is the mass of an electron, and hence calculate the momentum of an electron. $\left(m_{\mathrm{e}}=9.11 \times 10^{-31} \mathrm{~kg}\right)$
MEDIUM
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
The diagram shows the principles of an electron tube used to demonstrate electron diffraction.
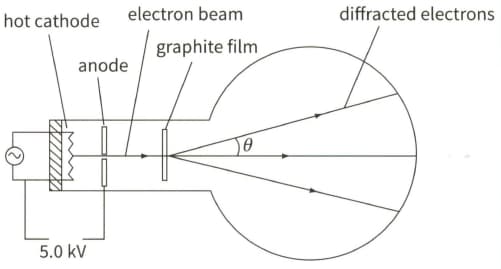
Calculate the de Broglie wavelength of the electrons.
EASY
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
Explain how the wavelengths of neutrons and electrons moving with the same energy would compare.
EASY
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
Describe the importance of the Planck constant in describing the behaviour of electromagnetic radiation and of electrons.
