The diameter of a cylinder is measured using Vernier calipers with no zero error. It is found that the zero of the Vernier scale lies between and of the main scale. The Vernier scale has divisions equivalent to . The division of the Vernier scale exactly coincides with one of the main scale divisions. The diameter of the cylinder is

Important Questions on Experiments in Physics
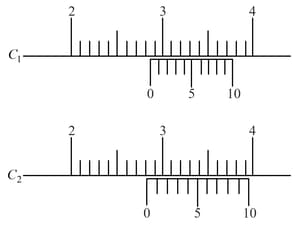
There are two Vernier calipers both of which have divided into equal divisions on the main scale. The Vernier scale of one of the calipers has equal divisions that correspond to main scale divisions. The Vernier scale of the other caliper has equal divisions that correspond to main scale divisions. The readings of the two calipers are shown in the figure. The measured values (in ) by calipers and , respectively, are
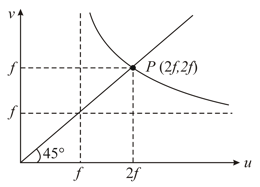
In an optics experiment, with the position of the object fixed, a student varies the position of a convex lens and for each position, the screen is adjusted to get a clear image of the object. A graph between the object distance and image distance , from the lens, is plotted using the same scale for the two axes. A straight line passing through the origin and making an angle of with the -axis meets the experimental curve at . The coordinates of will be
Main scale reading :
Circular scale reading : divisions
Given that on main scale corresponds to divisions of the circular scale. The diameter of wire from the above data is :
