The diameter of a plano-convex lens is and thickness at the centre is . If speed of light in material of lens is , the focal length of the lens is:

Important Questions on Refraction of Light at Spherical Surfaces : Lenses
Two identical glass rods and (refractive index ) have one convex end of radius of curvature .
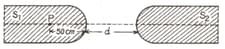
They are placed with the curved surfaces at a distance as shown in the figure, with their axes (shown by the dashed line) aligned. When a point source of light is placed inside rod on its axis at a distance of from the curved face, the light rays emanating from it are found to be parallel to the axis inside . The distance is:
Two identical thin plano-convex lenses (refractive index ) each having radius of curvature of are placed with their convex surfaces in contact at the centre. The intervening space is filled with the oil of refractive index . The focal length of the combination is:
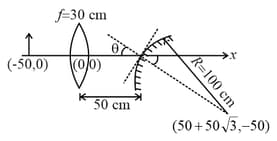
A small object is placed to the left of thin convex lens of focal length . A convex spherical mirror of radius of curvature is placed to the right of the lens at a distance of . The mirror is tilted such that the axis of the mirror is at an angle to the axis of the lens, as shown in the figure. If the origin of the coordinate system is taken to be at the centre of the lens, the coordinates (in cm) of the point () at which the image is formed are:
A convex lens is put from a light source and it makes a sharp image on a screen, kept from the lens. Now a glass block (refractive index ) of thickness is placed in contact with the light source. To get the sharp image again, the screen is shifted by a distance . Then is:
