The distance of an object from a spherical mirror is equal to the focal length of the mirror. Then the image :

Important Questions on Ray Optics
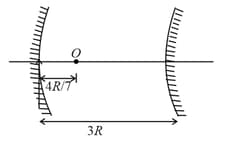
A concave mirror of focal length is cut into two parts from the middle and the two parts are moved perpendicularly by a distance from the previous principal axis . The distance between the images formed by the two parts is:
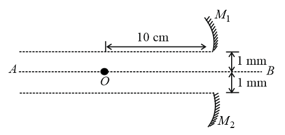
Radius of curvature of each mirror is . is object. Consider first reflection from concave mirror. Consider only first three reflection. The distance of final image from convex mirror is
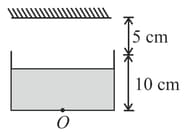
Consider the situation shown in figure. Water is filled a beaker upto a height of . A plane mirror is fixed at a height of from the surface of water. Distance of image from the mirror after reflection from it of an object at the bottom of the beaker is-
A plane mirror is placed at the bottom of a tank containing a liquid of refractive index . is a small object at a height above the mirror. An observer Vertically above ,outside the liquid sees and its image in the mirror. The apparent distance between these two will be:
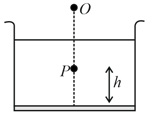
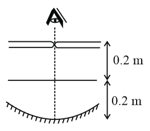
When a pin is moved along the principal axis of a small concave mirror, the image position coincides with the object at a point from the mirror, refer to figure. If the mirror is placed at depth of in a transparent liquid, the same phenomenon occurs when the pin is placed form the mirror. The refractive index of the liquid is: