EASY
Earn 100
The electrostatic potential due to a short electric dipole at a distance varies as:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Electrostatics
MEDIUM
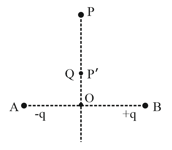
HARD
MEDIUM
HARD
EASY
EASY
HARD
Derive an expression for the electric potential at any point at a distance from the centre of an electric dipole. Hence find the potential if the point lies on
(i) axial line and (ii) equatorial line
EASY
EASY
HARD
An electric dipole is formed by two charges and located in -plane at and , respectively, as shown in the figure. The electric potential at point due to the dipole is . The charges and are then moved to the points and , respectively. What is the value of electric potential at due to the new dipole?
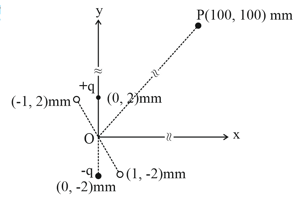
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
Determine the electric dipole moment of the system of three charges, placed on the vertices of an equilateral triangle, as shown in the figure:
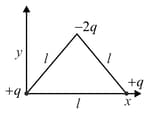
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
HARD
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
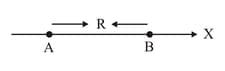
The distance from at which both of them produce the same potential is:

