The element sodium can emit light at two wavelengths, and . The light from sodium is being used in a Michelson interferometer, as shown in the below figure. Through what distance must mirror be moved if the shift in the fringe pattern for one wavelength is to be fringes more than the shift in the fringe pattern for the other wavelength?

Important Questions on Interference
Add the following quantities using the phasor method,
, and
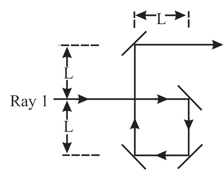
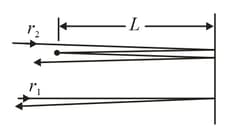
In the following figure, a light wave along ray , reflects once from a mirror and a light wave along ray , reflects twice from that same mirror and once from a tiny mirror at distance from the bigger mirror. (Neglect the slight tilt of the rays.) The waves have wavelength and are initially in phase.
What is the smallest value of that puts the final light waves exactly out of phase?
With the tiny mirror initially at that value of , how far must it be moved away from the bigger mirror to again put the final waves out of phase?
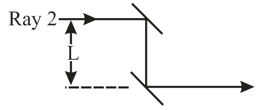
A light wave along ray reflects once from a mirror, and a light wave along ray reflects twice from that same mirror and once from a tiny mirror at distance from the bigger mirror. (Neglect the slight tilt of the rays.) The waves have wavelength and are initially exactly out of phase. What are the smallest, second smallest and fourth smallest values of , that result in the final waves being exactly in phase?
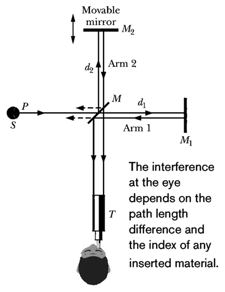
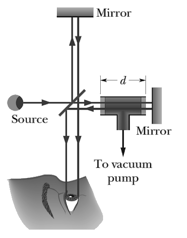
In the following figure, an airtight chamber of length is placed in one of the arms of a Michelson interferometer. (The glass window on each end of the chamber has negligible thickness.) Light of wavelength is used. Evacuating the air from the chamber causes a shift of bright fringes. From this data and to six significant figures, find the index of refraction of air at the atmospheric pressure.
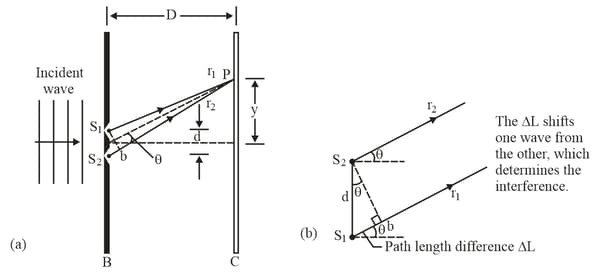
In the double-slit experiment, as shown in the following figure, the viewing screen is at distance . Point lies at distance from the centre of the pattern, the slit separation is , and the wavelength is .
(a) Determine where point is in the interference pattern by giving the maximum or minimum on which it lies, or the maximum and minimum between which it lies.
(b) What is the ratio of the intensity at point to the intensity at the centre of the pattern?
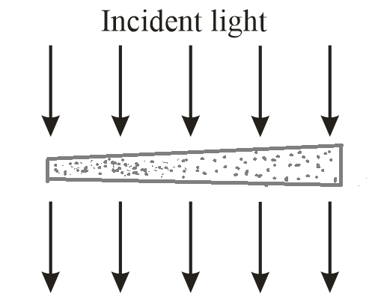
In the below figure, a broad beam of light of wavelength is incident at on a thin, wedge-shaped film with an index of refraction . The transmission gives bright and dark fringes along the film's length. What is the left-to-right change in the film thickness?
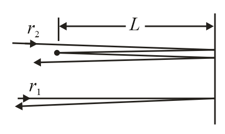
In the below figure, two light rays go through different paths by reflecting from the various flat surfaces shown. The light waves have a wavelength of and are initially in phase. What is the smallest and the second smallest value of distance that will put the waves exactly out of phase as they emerge from the region?