The elevation of boiling point and depression of freezing point of a certain solution of a monobasic acid in benzene are and , respectively. exists usually as a monomer, but it dissociates into ions (with degree of dissociation ) at the boiling point of the solution, whereas at the freezing point of the solution, exists as with a fixed value of . The molal boiling point elevation constant and molal freezing point depression constant are $K_{b}$ and , respectively. The correct expression for is
Important Questions on Solutions
for water is
[Assume ionisation of the complex and coordination number of as and that all molecules are present inside the coordination sphere]
is dissociated in water to and . The boiling point of molal aqueous solution of is-- . (Round off to the Nearest Integer).
[Given : Molal elevation constant of water boiling point of pure water]
A solute dimerizes in water. The boiling point of a molal solution of is . The percentage association of is ___ .
(Round off to the Nearest integer)
Use : for water
Boiling point of water
The plot given below shows curves (where, is the pressure and is the temperature) for two solvents and and isomolal solutions of in these solvents. completely dissociates in both the solvents.
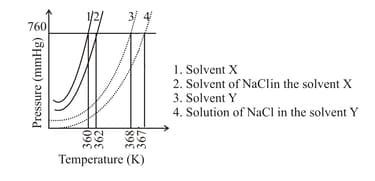
On the addition of equal number of moles of a non-volatile solute in equal amount (in ) of these solvents, the elevation of boiling point of solvent is three times that of solvent . The solute is known to undergo dimerization in these solvents. If the degree of dimerization is in the solvent , the degree of dimerization in the solvent is _______.

