The equation below describes the reaction of propanone with iodine. Hydrogen ions catalyse this reaction. . The progress of the reaction can be followed by using a calorimeter. The brown colour of the iodine fades as the reaction proceeds. The experimental results are shown in Table below.
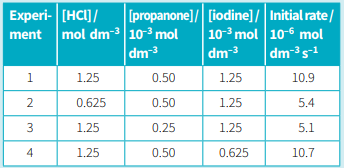
Use your rate equation and the information in Table (experiment 1) to calculate a value for the rate constant for this reaction.


Important Questions on Reaction Kinetics
An acidified solution of hydrogen peroxide reacts with iodide ions.
The rate equation for this reaction is rate . The mechanism below has been proposed for this reaction.
Explain why this mechanism is consistent with the rate equation.
The reaction is carried out in a sealed tube. At the start of the experiment, the concentration of both and , was The reaction is second order with respect to and first order with respect to . Which one of these represents the rate of reaction when the concentration of falls to ?
State whether the below given pair of substances might catalyse the reaction:
Explain your answer.
Given : of is and of is .
State whether the below given pair of substances might catalyse the reaction:
Explain your answer.
Given : of is and of is .
State whether the below given pair of substances might catalyse the reaction:
Explain your answer.
Given : of is and of is .
State whether the below given pair of substances might catalyse the reaction:
Explain your answer.
Given : of is and of is .
Describe in terms of oxidation number change, which species are being oxidised and which are being reduced in following equation:
Describe in terms of oxidation number change, which species are being oxidised and which are being reduced in following equation:
