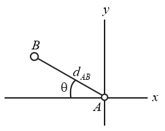
The figure shown below gives the potential energy function of a projectile, plotted outward from the surface of a planet of radius . If the projectile is launched radially outward from the surface with mechanical energy of , what are (a) its kinetic energy at radius and (b) its turning point in terms of ?


Important Questions on Gravitation
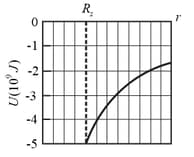
In the figure shown below, three spheres are located at distances and . What are the (a) magnitude and (b) direction (relative to the positive direction of the -axis) of the net gravitational force on sphere due to spheres and ?
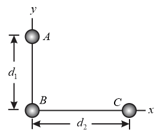
In the figure shown below, a square of edge length is formed by four spheres of masses and . In unit vector notation, what is the net gravitational force from them on a central sphere with mass ?
In deep space, sphere of mass is located at the origin of an -axis and sphere of mass is located on the axis at . Sphere is released from rest while sphere is held at the origin.
What is the gravitational potential energy of the two sphere system just as is released?
What is the kinetic energy of when it has moved towards ?
In , Galileo used his telescope to discover four moons around Jupiter, with these mean orbital radii and periods :
| Name | ||
| Io | ||
| Europa | ||
| Ganymede | ||
| Callisto |
Plot against , and show that you get a straight line.
Measure the slope of the line and compare it with the value that you expect from Kepler's third law.
Find the mass of Jupiter from the intercept of this line with the -axis.
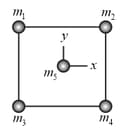
Three identical stars of mass form an equilateral triangle that rotates around the triangle's centre as the stars move in a common circle about that centre. The triangle has edge length . What is the speed of the stars?
Three point particles are fixed in position in an -plane. Two of them, particle of mass and particle of mass , are shown in figure, with a separation of at angle . Particle with mass is not shown. The net gravitational force acting on particle due to particles and is at an angle of from the positive direction of the -axis. What are the coordinate and the coordinate of particle ?