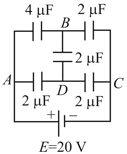
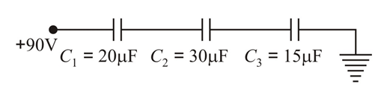The figure shows a diagonal symmetric arrangement of capacitors and a battery. If the potential of is zero, then (All the capacitors are initially uncharged)


Important Questions on Capacitance
Two capacitors of are charged to respectively. The plates of a capacitor are connected as shown in the discharged capacitor of capacity falls to the free ends of the wire and connected through the free ends of the wire, Then :

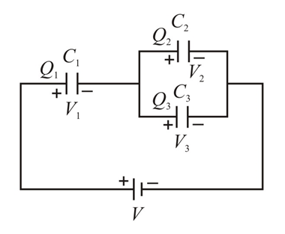
In the adjoining diagram all the capacitors are initially uncharged, they are connected with a battery as a shown in figure. Then
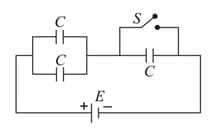
In the circuit shown in the figure, each capacitor has a capacitance . The emf of the cell is and circuit already in steady-state. If the switch is closed.
Two similar condensers are connected in parallel and are charged to a potential . Now, these are separated out and are connected in series. Then,
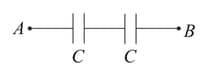
We have a combination as shown in the following figure. Choose the correct options.