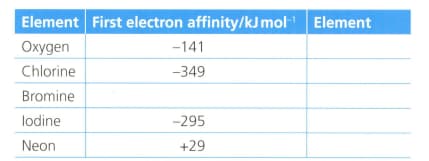
The first electron affinity is the energy change when one mole of gaseous atoms gains a mole of electrons. The table below shows the first electron affinity for selected atoms.

Explain the reason for the relative sizes of the values of the electron affinity for all the elements.


Important Questions on Why do Electrons Matter?
The first electron affinity is the energy change when one mole of gaseous atoms gains a mole of electrons. The table below shows the first electron affinity for selected atoms.

Explain the meaning of the following sentence: "the first electron affinity of oxygen is ."
The first electron affinity is the energy change when one mole of gaseous atoms gains a mole of electrons. The table below shows the first electron affinity for selected atoms.
The equation for the first electron affinity of oxygen is .
Formulate an equation (with state symbols) for the second electron affinity of oxygen.
The first electron affinity is the energy change when one mole of gaseous atoms gains a mole of electrons. The table below shows the first electron affinity for selected atoms.

Explain why, in terms of electrostatics, oxygen has a lower first electron affinity than chlorine.
The first electron affinity is the energy change when one mole of gaseous atoms gains a mole of electrons. The table below shows the first electron affinity for selected atoms.

In terms of electrostatics, oxygen has a lower first electron affinity than chlorine.
Explain why neon has a positive value of electron affinity.
A hydrogen atom has the main energy levels (shells) shown in the diagram below. refers to the shell number. This is the Bohr model of the atom.

Describe the electron transition (movement) within the hydrogen atom using the shell numbers indicated above, that will release the most energy.
A hydrogen atom has the main energy levels (shells) shown in the diagram below. refers to the shell number. This is the Bohr model of the atom.

Describe the electron transition (movement) within the hydrogen atom using the shell numbers indicated above, that will absorb the least energy.
A hydrogen atom has the main energy levels (shells) shown in the diagram below. refers to the shell number. This is the Bohr model of the atom.

List these electron transitions in order of increasing wavelength of light absorbed or emitted:
- to
- to
- to
- to
A hydrogen atom has the main energy levels (shells) shown in the diagram below. refers to the shell number. This is the Bohr model of the atom.

Explain why a ladder is a good analogy or model for visualising the energy levels of atoms (and molecules), and what are the limitations of the analogy.
