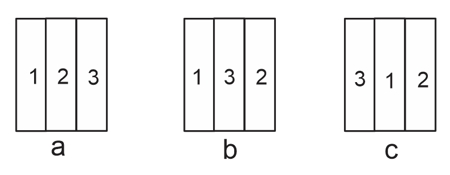
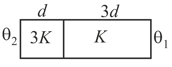
The following figure shows three different arrangements of materials 1,2, and 3 to form a wall. Thermal conductivities are . The left side of the wall is higher than the right side. Temperature difference across the material 1 has following relation in three cases

Important Questions on Thermal Properties of Matter
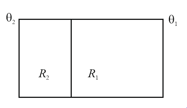
| Heat flow | Electrostatics |
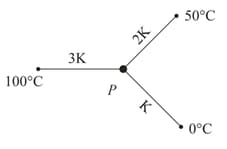
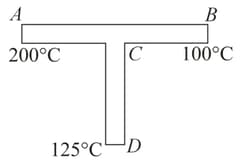
Three rods of same dimensions have thermal conductivities and . They are arranged as shown in the figure below. Then in the steady state the temperature of the junction is
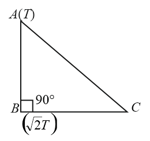
A rod of thermal resistance is joined at the middle of an identical rod as shown in figure. The ends and are maintained at and respectively. The heat current in is . The value of is
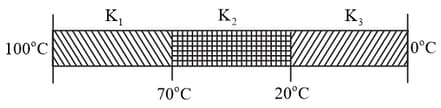
Three rods of identical cross-section and length are made of three different materials of thermal conductivity and , respectively. They are joined together at their ends to make a long rod (see figure). One end of the long rod is maintained at and the other at (see figure). If the joints of the rod are at and in steady and there is no loss of energy from the surface of the rod, the correct relationship between and is :
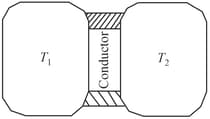
A thin piece of thermal conductor of constant thermal conductivity insulated on the lateral sides connects two reservoirs which are maintained at temperatures, and, as shown. Assuming that the system is in steady-state, which of the following plots best represents the dependence of the rate of change of entropy on the ratio of temperatures,
A piece of metal and a piece of wood are kept at a temperature of .
On touching the two with hand,
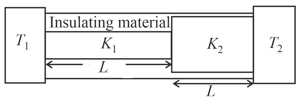
Consider a pair of insulating blocks with thermal resistances , and as shown in the figure. The temperature at the boundary between the two blocks is