EASY
Earn 100
The forward rate constant for the elementary reversible gaseous reaction
What is the rate constant for the backward reaction at this temperature if 10-4 moles of CH3 and 10 moles of C2H6 are present in a 10 litre vessel at equilibrium.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Equilibrium
HARD
MEDIUM
moles each of hydrogen and iodine is heated in a sealed ten litre vessel.At equilibrium, moles of were found. The equilibrium constant for is ........
MEDIUM
| Initial Concentration (A) | Initial Concentration (B) | Initial rate of formation of C |
|---|---|---|
The rate law for the formation of is
EASY
The value of for the reaction:
is Calculate the value of in .
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
HARD
(At )
EASY
EASY
The rate of this reaction is increased by
MEDIUM
When and are compared at It is found that
EASY
the equilibrium constant at is . Calculate for the reaction at temperature
MEDIUM
The value of for the reaction
The value of for the following reaction is :
MEDIUM
EASY
(assuming ideality)
EASY
at is If the equilibrium concentration of is the concentration of in is
EASY
.....(1)
.....(2)
The relation between and is:
MEDIUM
EASY
For the reaction:
is
HARD
The reaction
is in equilibrium in a closed vessel at The partial pressure (in atm) of in the reaction vessel is closest to:
[Given: The change in Gibbs energies of formation at and bar for
Gas constant ]
EASY
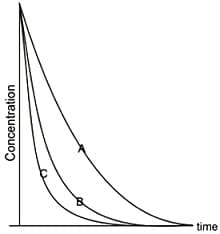
These profiles imply that the decay constants and follow the order

