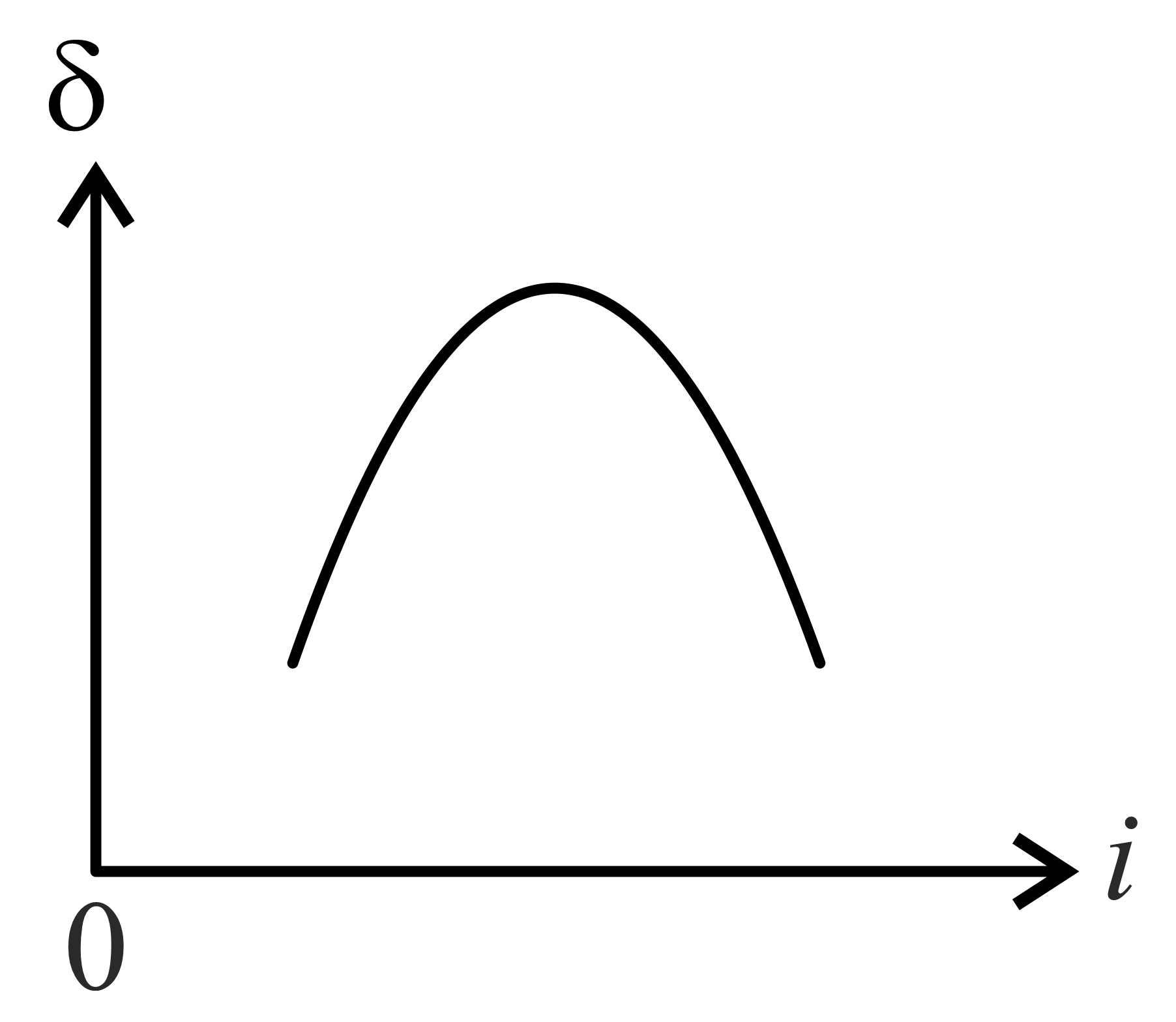
The graph between angle of deviation and angle of incidence for a triangular prism is represented by:

Important Questions on Ray Optics
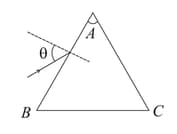
Monochromatic light is incident on a glass prism of angle . If the refractive index of the material of the prism is , a ray, incident at an angle , on the face would get transmitted through the face of the prism provided.
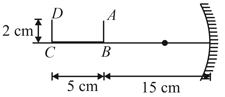
A U-shaped wire is placed before a concave mirror having radius of curvature as shown in the figure. Find the total length of the image.
(i) A paperweight of refractive index in the form of a hemisphere of the radius is used to hold down a printed page. An observer looks at the page vertically through the paperweight. At what height above the page will the printed letters near the centre appear to the observer? (ii) Solve the previous problem if the paperweight is inverted at its place so that the spherical surface touches the paper.
