The graph shows the heating curve for a pure substance. The temperature rises with time as the substance is heated.
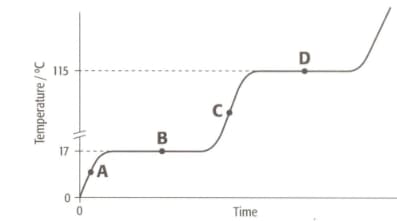
What is the physical state(s) of a substance at point C?


Important Questions on The Nature of Matter
The graph shows the heating curve for a pure substance. The temperature rises with time as the substance is heated.
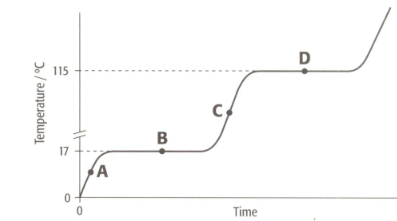
What is the physical state(s) of a substance at point D?
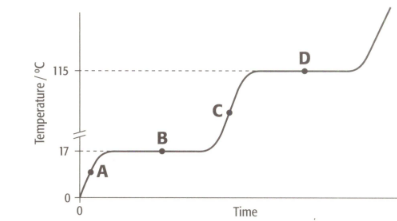
What is the melting point of the substance?
(A) (B) (C)
Enter your correct answer as A, B or C.
The graph shows the heating curve for a pure substance. The temperature rises with time as the substance is heated.
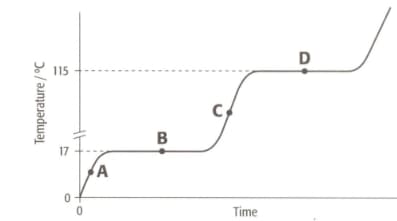
What is its boiling point?
(A) (B) (C)
Enter your correct answer as A, B or C.
The graph shows the heating curve for a pure substance. The temperature rises with time as the substance is heated.
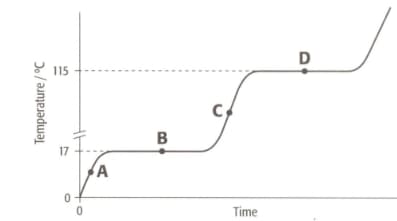
What happens to the temperature while the substance is changing state?
The graph shows the heating curve for a pure substance. The temperature rises with time as the substance is heated.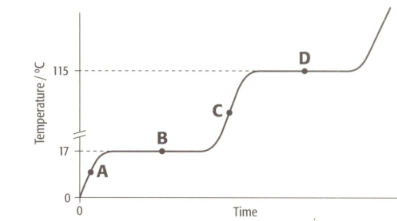
The substance is not water. How do we know from this graph?
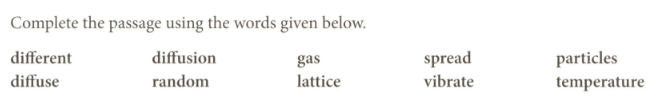
The kinetic model states that the _____ in a liquid and a _____ are in constant motion. In a gas, the particles are far apart from each other and their motion is said to be _____. The particles in a solid are held in fixed positions in a regular _____. In a solid, The particles can only _____ about their fixed positions.
Liquids and gases are fluid states. When particles move in a fluid they can collide with each other. When they collide, they bounce of each other in _____ directions. If two gases are liquids are mixed, the different type of particle _____ out and mixed up. This process is called _____.
At the same _____ particles that have lower mass move faster than those with higher mass. This means that the lighter particles spread and mix more quickly; the lighter particles are said to _____ faster than the heavier particles.
Use the data given for the substances listed below to answer the question that follows on its physical state at its room temperature of and atmospheric pressure.
| Substance | Melting point/ | Boiling point/ |
| sodium | 98 | 883 |
| radon | -71 | -62 |
| ethanol | -117 | 78 |
| cobalt | 1492 | 2900 |
| nitrogen | -210 | -196 |
| propane | -188 | -42 |
| ethanoic acid | 16 | 118 |
Which substance is a liquid over the smallest range of temperature?
Use the data given for the substances listed below to answer the question that follows on its physical state at its room temperature of and atmospheric pressure.
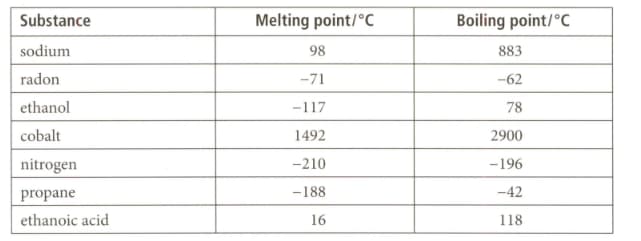
Which two substances are gaseous at .
