The household supply of electricity is at (RMS value) and . Find the peak voltage and the least possible time in which the voltage can change from the RMS value to zero.

Important Points to Remember in Chapter -1 - Alternating Current from H C Verma CONCEPTS OF PHYSICS [VOLUME 2] Solutions
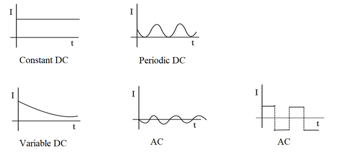
(i) A current that changes its direction periodically is called alternating current (). If a current maintains its direction constant it is called direct current ().
(ii) Average value:
(iii) RMS value:
(iv) For a sinusoidal voltage , where is the peak voltage, is the angular frequency of the source.
(v) For a sinusoidal current , where is the peak current.
2. AC generator:
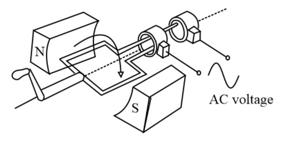
An generator is an electric generator that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy in form of an alternative emf or alternating current. generators work on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
3. AC circuit:
 |
 |
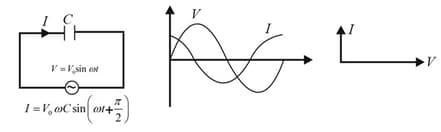 |
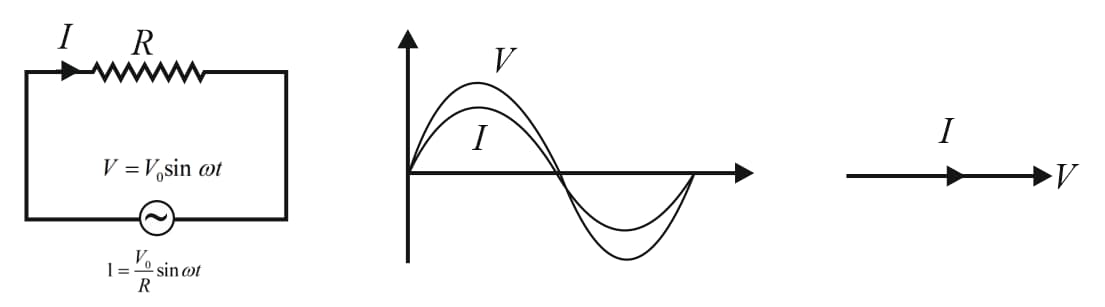
(i) In a pure resistor, current and voltage are in phase.
(ii) In a pure capacitor, the current leads the voltage by
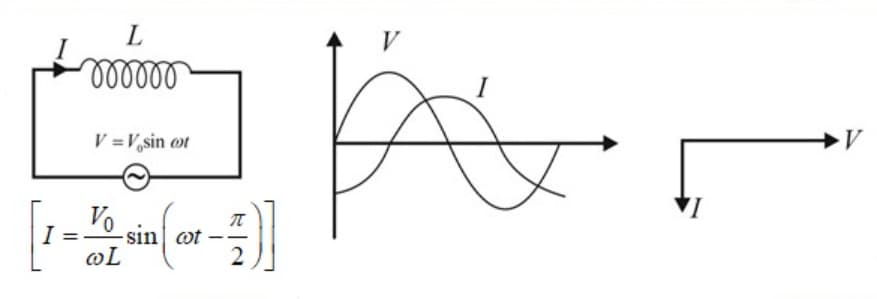
(iii) In a pure inductor, the current lags the voltage by
4. Reactance and Impedance:
(i) is called inductive reactance and is denoted by
(ii) is called capacitive reactance and is denoted by
5. Series LCR Circuit:
Consider a series series circuit with resistance , inductive reactance , and capacitive reactance .
(i) Impedance,
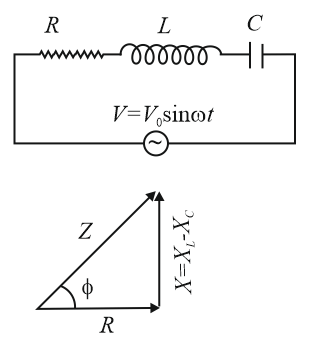
(ii) Applied voltage in terms of voltages across the components,
6. Power in AC Circuits and Wattless current:
(i) Average power consumed in a cycle
(ii) , here is called a power factor.
(iii) The current in circuit is said to be wattless current when the average power consumed in such circuit corresponding to zero such current is also called idle current.
7. Wattless current:
In an circuit, if the average power consumed is zero, then the current is called a wattless current. Its formula is , where is the phase difference between current and voltage applied.
8. Resonance:
(i) At resonance:
(ii) Resonant frequency is , where is the inductance, and is capacitance.
(iii) Nature of the circuit is resistive.
(iv) Current in the circuit is maximum, i.e.,
(v) Power consumed at resonance is
9. Bandwidth:
The bandwidth of series circuit of resistance , inductance , and Capacitance is
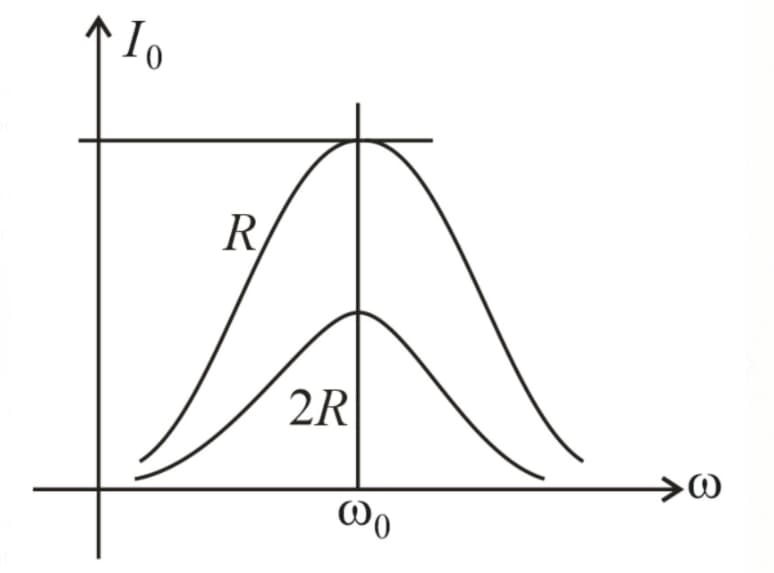
As the resistance increases, peak current decreases, and the bandwidth increases.
10. Quality factor:
(i) factor (also known as a Quality factor or -factor) is defined as a dimensionless parameter that describes the underdamped condition of an oscillator or resonator.
(ii) The quality factor of series RLC circuit of resistance , inductance , and Capacitance is
11. LC oscillations:
(i) Charge at time is , and current at time is , where maximum current .
is the maximum charge on the capacitor, and is the angular frequency with which the current ocillates.
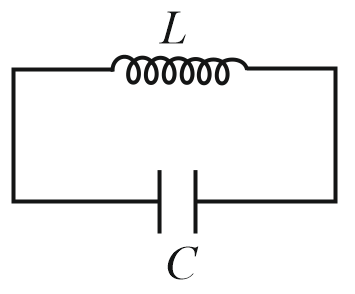
(ii) Energy , where is inductance, and is the capacitance.
(iii) Comparison of oscillations with of spring:
12. Comparison of damped mechanical & electrical systems:
(i) Series circuit:
Consider a resistance , inductnace , and capacitance are connected in series. Let be the charge on the capacitor at time . Then,
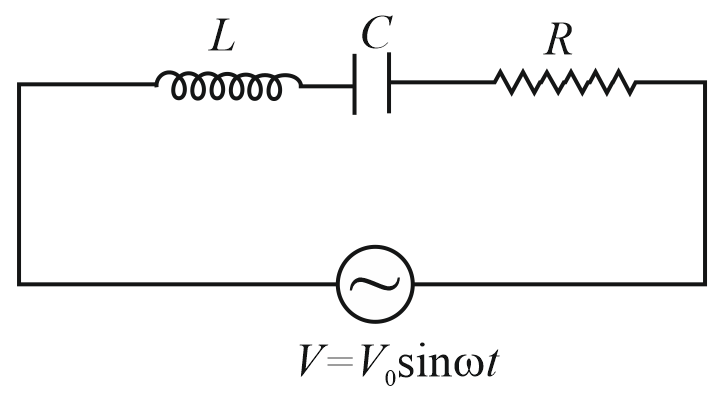
compare with the mechanical damped system equation,
, where damping coefficient.
| Mechanical system | Electrical systems (series ) |
| Displacement | Charge |
| Driving force | Driving voltage |
| Kinetic energy | Electromagnetic energy of moving charge |
| Potential energy | The energy of the static charge |
| Mass | Inductance |
| Power | Power |
| Damping | Resistance |
| Spring constant |
(ii) Parallel circuit:
(a) Consider a resistance , inductnace , and capacitance are connected in parallel. Let be the charge on the capacitor at time . Then,
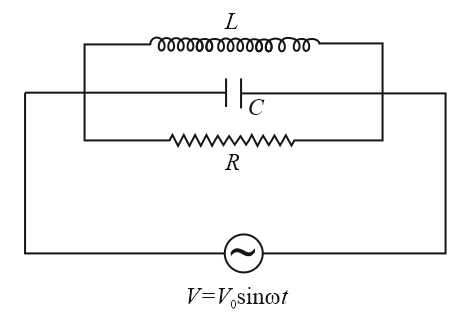
(b) Displacement Flux linkage
(c) Velocity Voltage
(d) Mass Capacitance
(e) Spring constant Reciprocal Inductance
(f) Damping coefficient Reciprocal resistance ; Driving force Current
