The image of a square hole on a screen illuminated by light is obtained on another screen with the help of a converging lens. The distance of the illuminated square from the lens is . The area of the image is times that of the square hole. Calculate the position of the image and the focal length of the lens.

Important Questions on Refraction at Spherical Surfaces and Spherical Lens
A thin Plano-convex lens of focal length $f$ is split into two halves; one of the halves is shifted along the optical axis [Fig. 14.71]. The separation between object and image is $1.8 \mathrm{~m}$. The magnification of the image formed by one of the half-lenses is . Find the focal length of the lens and the separation between the two halves. Draw the ray diagram for image formation.

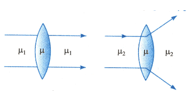
What is relation between the refractive index and If the behaviour of light rays is as shown in the Fig.
The radius of curvature of the convex face of a Plano convex lens is and its . Find the focal length of the lens. The plane face of the lens is now silvered.
The radius of curvature of the convex face of a Plano convex lens is and its . The focal length of the lens is .The plane surface of the lens is coated with silver. At what distance from the lens will parallel rays incident on the convex surface converge?
The radius of curvature of the convex face of a Plano convex lens is and its . Sketch the ray diagram to locate the image, when a point object is placed on the axis from the lens.
