EASY
Earn 100
The interactions between species explains the conduit for energy transfer across trophic levels is
(a)Mutualism
(b)Competition
(c)Predation
(d)Commensalism
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Organisms and Populations
EASY
HARD
1) The human liver fluke, a nematode parasite, depends on two intermediate hosts (a snail and a fish) to complete its life cycle.
2) The malarial parasite needs a vector (mosquito) to spread to other host organisms.
3) In case of brood parasitism, the eggs of parasitic birds (e.g., cuckoo) are not detected and removed from the nest because the parasite's eggs resemble the host's eggs in morphology and colour.
4) A population of frogs protected from all predators would decrease indefinitely.
EASY
EASY
HARD
EASY
HARD
Given the graphs below, the interaction between species and can be classified as
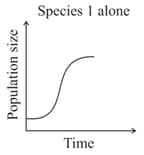
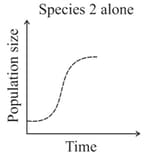
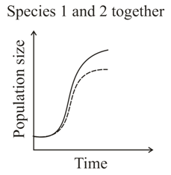
MEDIUM
Study the following table and pick up the correct combinations.
| S.No | Type of parasite | Lives in host | Example |
| I) | Cytozoic parasites |
Live among cells of tissues of host |
Plasmodium |
| II) | Histozoic parasites | Live within the host's cells | Wuchereria |
| III) | Coelozoic parasites | Live in cavities of host | Ascaris |
| IV) | Hyperparasites | Lives in the body of another parasite | Nosema |
MEDIUM

HARD
| Column-I | Column-II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Saprophyte | Symbiotic association of fungi with plant roots | ||
| Parasite | Decomposition of dead organic materials | ||
| Lichens | Living on living plants | ||
| Mycorrhiza | Symbiotic association of algae and fungi |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
MEDIUM
Match column-I with column-II and select the correct option.
| Column-I | Column-II | ||
| a) | Commensalism | i) | Lichen |
| b) | Mutualism | ii) | Plasmodium |
| c) | Parasitism | iii) | Hawk |
| d) | Predation | iv) | Orchid |
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
Assertion (A): The Monarch butterfly feeds on poisonous weeds during its caterpillar stage.
Reason (R): It helps butterfly to become distasteful to the predator.
EASY
MEDIUM
Study the following table and pick up the correct combinations.
| S.No. | Interaction | Species A | Species B |
| I) | Mutualism | ||
| II) | Competition | ||
| III) | Predation | ||
| IV) | Parasitism | ||
| V) | Commensalism | ||
| VI) | Amensalism |
EASY
Match the following?
| The list I | List II | ||
| (i) | Calotropis | (a) | Predator of Americana Pacific |
| (ii) | Cactus | (b) | Insects and frogs cryptically coloured |
| (iii) | Pisaster | (c) | Distasteful glycosides |
| (iv) | Monarch Butterfly | (d) | Cardiac glycosides |
| (v) | Camouflage | (e) | Predator is a moth |
EASY
EASY
HARD

