The isotope nitrogen- has a half-life of . A sample initially contains undecayed nuclei. Write down an equation to show how the number undecayed depends on time .

Important Questions on Nuclear Physics
The isotope nitrogen-13 has a half-life of . A sample initially contains undecayed nuclei. Calculate how many undecayed nuclei will remain after , and after .
The isotope nitrogen-13 has a half-life of . A sample initially contains undecayed nuclei. Determine how many nuclei will decay during the first .
A sample of an isotope for which contains undecayed nuclei at the start of an experiment. Determine the number of undecayed nuclei after .
A sample of an isotope for which contains undecayed nuclei at the start of an experiment. Determine its activity after .
The value of for protactinium- is Table, shows the number of undecayed nuclei $N$ in a sample. Copy and complete Table. Draw a graph of N against t, and use it to find the half-life of protactinium-.
| t / s | 0 | 20 | 40 | 60 | 80 | 100 | 120 | 140 |
| N | 400 | 330 |
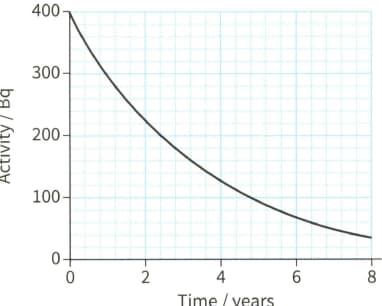
Figure shows the decay of an isotope of caesium, . Use the graph to determine the half-life of this nuclide in years, and hence find the decay constant in .
The isotope decays with a half-life of . Calculate the decay constant for this nuclide.
