The lattice energy of magnesium bromide, can be calculated using the enthalpy changes shown in the table.
Type of enthalpy change
Value /
first ionisation energy of magnesium
second ionisation energy of magnesium
first electron affinity of bromine
enthalpy change of formation of
enthalpy change of atomisation of magnesium
enthalpy change of atomisation of bromine
State the meaning of the term second ionisation energy.

Important Questions on Lattice Energy
The lattice energy of magnesium bromide, can be calculated using the enthalpy changes shown in the table.
| Type of enthalpy change | Value / |
| first ionisation energy of magnesium | |
| second ionisation energy of magnesium | |
| first electron affinity of bromine | |
| enthalpy change of formation of | |
| enthalpy change of atomisation of magnesium | |
| enthalpy change of atomisation of bromine |
Draw and label a Born-Haber cycle to calculate the lattice energy of magnesium bromide and calculate the lattice energy of magnesium bromide.
For the pair and , state with reasons, which one you would expect to have the higher lattice energy.
For the pair and , state with reasons, which one you would expect to have the higher lattice energy.
In some crystal lattices, some of the ions are polarised. State the meaning of the term ion polarisation.
In some crystal lattices, some of the ions are polarised. Explain why a magnesium ion is better than a sodium ion at polarising an iodide ion.
The diagram shows the enthalpy changes when sodium chloride is dissolved in water.
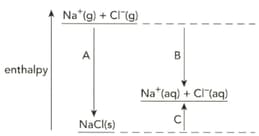
Define the term enthalpy change of solution.
The diagram shows the enthalpy changes when sodium chloride is dissolved in water.
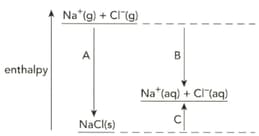
Define the term enthalpy change of hydration.
