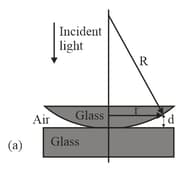
The lens in Newton's rings experiment (see figure) has diameter and For in air, how many bright rings are produced with the setup (a) in air and when immersed in water



Important Questions on Interference
A Newton's ring apparatus is to be used to determine the radius of curvature of a lens (see figure). The radii of the and bright rings are found to be and respectively, in light of wavelength . Calculate the radius of curvature of the lower surface of the lens.
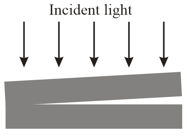
In Figure a broad beam of light of wavelength is sent directly downward through the top plate of a pair of glass plates touching at the left end. The air between the plates acts as a thin film, and an interference pattern can be seen from above the plates. Initially, a dark fringe lies at the left end, a bright fringe lies at the right end, a bright fringe lies at the right end and nine dark fringes lie between those two end fringes. The plates are then very gradually squeezed together at a constant rate to decrease the angle between them. As a result, the fringe at the right side changes between being bright to being dark every (a) At what rate is the spacing between the plates at the right end being changed? (b) By how much has the spacing there changed when both left and right ends have a dark fringe and there are five dark fringes between them?
In the figure below two microscope slides touch at one end and are separated at the other end. When light of wavelength shines vertically down on the slides, an overhead observer sees an interference pattern on the slides with the dark fringes separated by What is the angle between the slides?
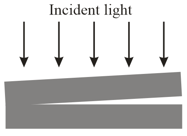
In the figure, a broad beam of monochromatic light is directed perpendicularly through two glass plates that are held together at one end to create a wedge of air between them. An observer intercepting the light reflected from the wedge of air, which acts as a thin film, sees dark fringes along the length of the wedge. When the air between the plates is evacuated, only dark fringes are seen. Calculate to six significant figures the index of refraction of air from these data.
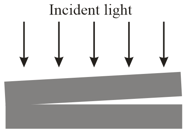
In the figure below, a broad beam of light of wavelength is sent directly downward through the top plate of a pair of glass plates. The plates are long, touch at the left end, and are separated by at the right end. The air between the plates acts as a thin film. How many bright fringes will be seen by an observer looking down through the top plate?
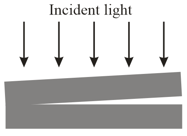
Two rectangular glass plates are in contact along one edge and are separated along the opposite edge (Figure). Light with a wavelength of is incident perpendicularly onto the top plate. The air between the plates acts as a thin film. Nine dark fringes and eight bright fringes are observed from above the top plate. If the distance between the two plates along the separated edges is increased by how many dark fringes will there then be across the top plate?
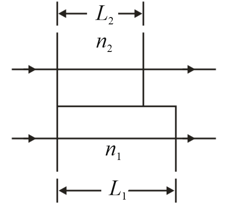
Two waves of light in air, of wavelength are initially in phase. Then they both travel through a layer of plastic as shown in the figure with and (a) What multiple of gives their phase difference after they both have emerged from the layers? (b) If the waves later arrive at some common point with the same amplitude, is their interference fully constructive, fully destructive, intermediate but closer to fully constructive, or intermediate but closer to fully destructive?