The magnitude of angular momentum, orbit radius and frequency of revolution of electron in hydrogen atom corresponding to quantum number are and respectively. Then according to Bohr's theory of hydrogen atom

Important Questions on Atomic Physics
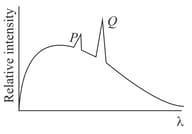
In the characteristic -ray spectra given in the figure of some atom superimposed on continuous -ray spectra
Statement- : The Bohr model of the hydrogen atom does not explain the fine structure of spectral lines.
and
Statement-: The Bohr model does not take into account the spin of the electron
Statement- : The Bohr model of the hydrogen atom does not explain the fine structure of spectral lines.
and
Statement-: The Bohr model does not take into account the spin of the electron
A single electron orbits a stationary nucleus of charge Ze where Z is a constant and is the electronic charge. It requires to excite the electron from the Bohr orbit to Bohr orbit. Find
(i) the value of Z,
(ii) energy required to excite the electron from the third to the fourth orbit.
(iii) the wavelength of radiation required to remove the electron from the first orbit to infinity
(iv) the kinetic energy, potential energy and angular momentum in the first Bohr orbit.
(v) the radius of the first Bohr orbit.
