The oxygen-binding capacity of hemoglobin is affected by pH. The saturation curve of hemoglobin at normal physiological pH is given in figure below.
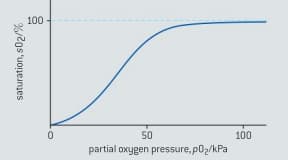
Sketch the saturation curve of hemoglobin at pH .


Important Questions on Biochemistry
Explain, in terms of enzyme inhibition, the effects of protons and carbon monoxide on the saturation curve of hemoglobin.
One of the organic compounds shown in figure below is colourless while the other is orange.
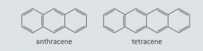
Predict, with reference to conjugation of double bonds, which compound (anthracene or tetracene) will absorb visible light and, therefore, be coloured.
The pigment in blueberries is an anthocyanin. With reference to the colour wheel, explain how the pigment in blueberries causes them to be blue.
State the combination of pH and temperature that produces the strongest colour in anthocyanins.
The absorption spectrum of carotene is shown in figure below.
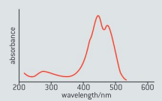
In terms of this spectrum, explain why carotenes have their typical colour.
The wavelength of visible light lies between and . The absorption spectrum of a particular anthocyanin is shown in figure below.
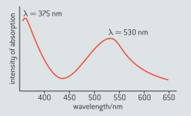
Explain what effect, if any, the absorption at will have on the colour of the anthocyanin
The wavelength of visible light lies between and . The absorption spectrum of a particular anthocyanin is shown in figure below.
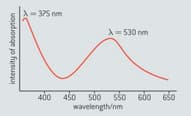
Explain what effect, if any, the absorption at will have on the colour of the anthocyanin.
Anthocyanins, the pigments which occur naturally in many flowers and fruits, are water-soluble and often change colour as the temperature or pH changes. The below diagrams show two structures of the same anthocyanin under different conditions.
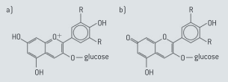
Explain why anthocyanins tend to be soluble in water.
