MEDIUM
12th West Bengal Board
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
The potential at a point (measured in ) due to some charges situated on the -axis is given by
volt.
The electric field at is given by
(a) and in the ve direction
(b) and in the ve direction
(c) and in the ve direction
(d) and in the ve direction
50% studentsanswered this correctly

Important Questions on Interaction of Charged Particles, Electric Field and Potential
HARD
12th West Bengal Board
IMPORTANT
Two point charges and are located at and respectively. The location of a point on the -axis is at which the net electric field due to these two point charges is zero is
HARD
12th West Bengal Board
IMPORTANT
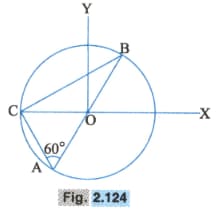
Consider a system of three charges and Placed at points and respectively, as shown in the figure, Fig. . Take to be centre of the circle of radius and angle
EASY
12th West Bengal Board
IMPORTANT
An electric dipole is placed at an angle of to a nonuniform electric field. The dipole will experience
EASY
12th West Bengal Board
IMPORTANT
Two points and are maintained at the potentials of and respectively. The work done in moving electrons from to is
MEDIUM
12th West Bengal Board
IMPORTANT
Two identical positive charges are fixed on the -axis at equal distance from the origin . A negatively charged particle starts on the -axis, at a large distance from , moves along -axis, passes through and moves far away from . Its acceleration is taken as positive along its direction of motion. The best graph, between the particle's acceleration and its -coordinate is represented by (see Fig. )
MEDIUM
12th West Bengal Board
IMPORTANT
An electric charge is placed at the origin of coordinate system. Two points and are situated at and respectively. The potential difference between the points and will be
HARD
12th West Bengal Board
IMPORTANT
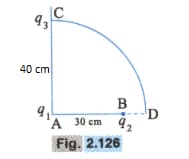
Two charges and are placed apart, as shown in Fig. . third charge is moved along the arc of a circle of radius from to . The charge in the potential energy of the system is , where is
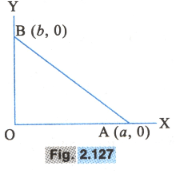
HARD
12th West Bengal Board
IMPORTANT
A charge is placed at the origin of axes as shown in Fig. . The work done in taking a charge from to along the straight line is