The potential energy of a diatomic molecule(a two-atom system like or ) is given by , where is the separation of the two atoms of the molecule and and are positive constants. This potential energy is associated with the force that binds the two atoms together. (a) Find the equilibrium separation - that is, the distance between the atoms at which the force on each atom is zero. Is the force repulsive (the atoms are pushed apart) or attractive (they are pulled together) if their separation is (b) smaller and (c) larger than the equilibrium separation?

Important Questions on Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy
A single conservative force, acts on a particle that moves along the -axis. The potential energy, associated with is given by, where, is in meters. At , the particle has a kinetic energy of .
(a) What is the mechanical energy of the system?
(b) Make a plot of as a function of for and on the same graph, draw the line that represents the mechanical energy of the system. Use part (b) to determine (c) the least value of the particle can reach and (d) the greatest value of the particle can reach. Use part (b) to determine (e) the maximum kinetic energy of the particle and (f) the value of at which it occurs.
(g) Determine an expression in newtons and meters for as a function of (h) For what (finite) value of is ?
A worker pushed a block along a level floor at a constant speed with a force directed below the horizontal. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the floor was , what were,
(a) The work done by the worker's force and
(b) The increase in thermal energy of the block- floor system?
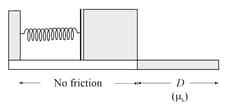
In the figure shown below, a block is accelerated from rest by a compressed spring of spring constant . The block leaves the spring at the spring's relaxed length and then travels over a horizontal floor with a coefficient of kinetic friction The frictional force stops the block in distance What are
(a) The increase in the thermal energy of the block-floor system
(b) The maximum kinetic energy of the block
(c) the original compression distance of the spring?
A horizontal force of magnitude pushes a block of mass across a floor where the coefficient of kinetic friction is
(a) How much work is done by that applied force on the block-floor system when the block slides through a displacement of across the floor?
(b) During that displacement, the thermal energy of the block increases by . What is the increase in thermal energy of the floor?
(c) What is the increase in the kinetic energy of the block?
(a) How much work is done by the truck engine in ?
(b) After the truck enters a hilly region whose inclination is and continues to move with the same speed for another What is the total work done by the engine during that period against the gravitational force and the frictional force?
(c) What is the total work done by the engine in the full ?
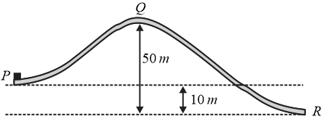
A small block of mass has an initial kinetic energy of while moving over the frictionless surface shown in figure.
(a) Find the kinetic energy of block at . (b) If we assume that the potential energy at is equal to zero, what is the potential energy of the block at ? (c) Find the speed of the block at . (d) Find the change in the potential energy as the block moves from to .
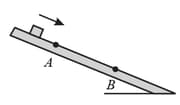
In the figure shown below, a block slides down an incline. As it moves from point to equal to force acts on the block, with magnitude directed down the incline. The magnitude of the frictional force acting on the block is . If the kinetic energy of the block increases by between and , how much work is done on the block by the gravitational force as the block moves from?