The radiant flux intensity from a star measured at the Earth is . The luminosity of the star is . Calculate the distance of this star from the Earth in metres.

Important Questions on Astronomy and Cosmology
(a) A student conducted the experiment from Practical Activity. The results from the experiment are shown below:
Use this data to estimate the diameter of the Sun.
Use the data given in Figure to show the validity of Wien's displacement law for and .
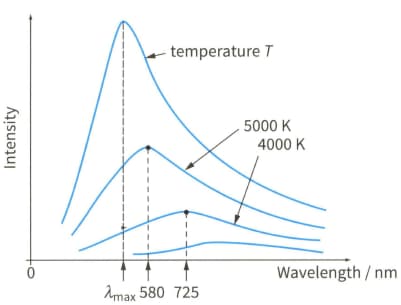
The intensity- wavelength graph depends on the temperature of the object. For an object at a thermodynamic temperature , the intensity against wavelength curve peaks at a wavelength .
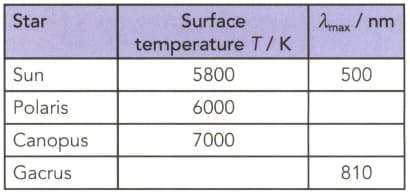
Use Wien's displacement law to complete the table. Write your answers to two significant figures.
The luminosity of the star Aldebaran is 520 times that of the Sun. The wavelength of light at peak intensity for Aldebaran is and the wavelength of light at peak intensity for the Sun is . Explain whether Aldebaran is cooler or hotter than the Sun. Radius of Aldebaran / radius of the Sun.
The luminosity of the star Aldebaran is 520 times that of the Sun. The wavelength of light at peak intensity for Aldebaran is and the wavelength of light at peak intensity for the Sun is .
(b) Calculate the ratio:
Radius of Aldebaran / radius of the Sun.
A galaxy is at a distance of from us and is moving away with a speed of . Calculate the Hubble constant based on this data.
