EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
The readings of a constant volume gas thermometer at 0C and 100C are 40cm of mercury and 60 cm of mercury. If its reading at an unknown temperature is 100cm of mercury column, then the temperature is
(a)100C
(b)25C
(c)300C
(d)None of these
70.83% studentsanswered this correctly

Important Questions on Thermal Properties of Matter
EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
The temperature at which Centigrade thermometer and Kelvin thermometer gives the same reading is,
EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
If the cold junction of a thermo-couple is kept at 0oC and the hot junction is kept at ToC then the relation between neutral temperature (Tn) and temperature of inversion (Ti) is
EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
What is the temperature at which we get the same reading, on both the Centigrade and Fahrenheit scales?
EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
The temperature of a body on kelvin scale is found to be . When it is measured by Fahrenheit thermometer, it is found to be , then the value of is
EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
A centigrade and a Fahrenheit thermometer are dipped in boiling water. The water temperature is lowered until the Fahrenheit thermometer registers . What is the fall in temperature as registered by the centigrade thermometer?
EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
Two metal rods of the same length have their coefficient of linear expansion in the ratio .
If the temperature of the first rod is raised by , then to keep their final length equal, the temperature of the second rod must be increased by:
MEDIUM
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
A pendulum clock (fitted with a small heavy bob that is connected with a metal rod) is seconds fast each day at a temperature of and seconds slow at a temperature of . The temperature at which it is designed to give the correct time is_____.
EASY
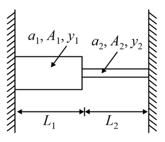
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
Two elastic rods are joined between fixed supports as shown in diagram. Condition for no change in the lengths of individual rods with the increase of temperature ( = linear expansion coefficient, A1, A2 = area of rods, y1, y2 = Young's modulus) is