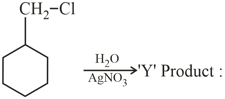EASY
Earn 100
The replacement of hydrogen atom(s) in an aliphatic hydrocarbon by halogen atom(s) results in the formation of alkyl halide (haloalkane).
(a)True
(b)False
100% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
HARD
The CORRECT match of compound in Column with density in Column is
| Column A | Column B | ||
| p | i. | ||
| q | ii. | ||
| r | iii. | ||
| s | iv. |
HARD
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
Represent the union of two sets by Venn diagram for each of the following.
is a prime number between and
is an odd number between and
MEDIUM
Classify the following compounds into haloalkanes and haloarenes:
and
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
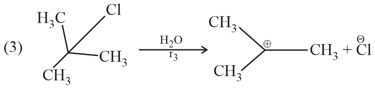
The product of the reaction give below is :
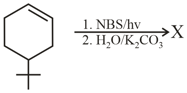
MEDIUM
Haloalkanes contain halogen atom(s) attached to the carbon atom of an alkyl group. The hybridisation of the carbon atom is _____.
(A)
(B)
(C)
Enter your correct answer as A, B or C.
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
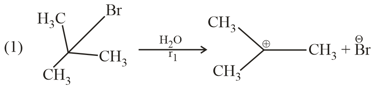
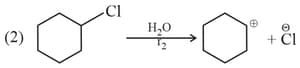
The rates and are in the order :
MEDIUM
EASY