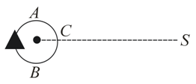MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
The second overtone of an open pipe and a closed pipe have the same frequencies. The ratio of the fundamental frequency of to the fundamental frequency of is
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
50% studentsanswered this correctly

Important Questions on Sound Waves
MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
EASY
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
HARD
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
EASY
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
EASY
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
An engine driver moving towards a wall with a velocity of emits a note of frequency . The frequency of note after reflection from the wall as heard by the engine driver when the speed of sound in air is is
HARD
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
EASY
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
An observer moves on a circle as shown in the figure and a small sound source is at . Let at , , be the frequencies heard when the observer is at , , and , respectively.