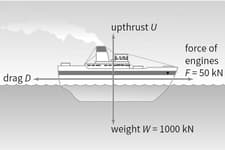
The ship shown in Figure is travelling at a constant velocity.
What is the upthrust Of the water?
The force Is the frictional drag of the water on the boat. Like air resistance, drag is always in the opposite direction to the object's motion.


Important Questions on Forces: Vectors and Moments
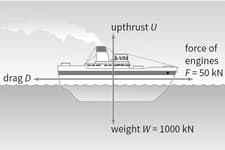
The ship shown in Figure is travelling at a constant velocity.
What is the drag of the water?
The force is the frictional drag of the water on the boat. Like air resistance, drag is always in the opposite direction to the object's motion.
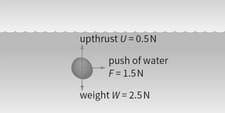
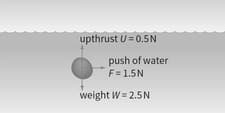
A stone is dropped into a fast-flowing stream. It does not fall vertically because of the sideways push of the water. Calculate the resultant force on the stone.
A stone is dropped into a fast-flowing stream. It does not fall vertically because of the sideways push of the water
Is the stone in equilibrium?
The person in Figure is pulling a large box using a rope. Use the idea of components of a force to explain why they are more likely to get the box to move if the rope is horizontal (as in a) than if it is sloping upwards (as in b ).
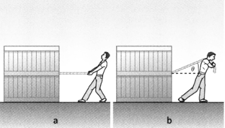
Why is it easier to move the box with the rope horizontal?
A crate is sliding down a slope. The weight of the crate is . The slope makes an angle of With the horizontal. Draw a diagram to show the situation. Include arrows to represent the weight of the crate and the contact force of the slope acting on the crate.
A crate is sliding down a slope. The weight of the crate is . The slope makes an angle of With the horizontal. Calculate the component of the weight down the slope.
A crate is sliding down a slope. The weight of the crate is . The slope makes an angle of with the horizontal. Explain why the contact force of the slope has no component down the slope.
A crate is sliding down a slope. The weight of the crate is . The slope makes an angle of with the horizontal. What third force might act to oppose the motion? In which direction would it act.