The standard free energy change and standard activation energy for four biochemical reactions are listed in the table below.
Reaction
Standard free energy change
Standard activation energy
P
-40
18
Q
-71
18
R
-40
11
S
-71
11
A few interpretations are given below. Among these, the most appropriate interpretation is;

Important Questions on Biomolecules
Refer to the given graph showing relationship between temperature and enzyme action.
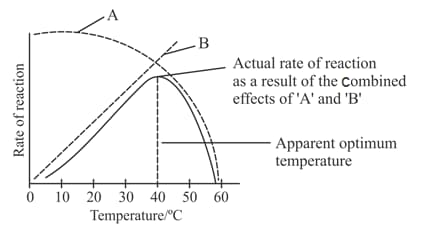
Select the correct statement regarding 'A' and 'B'.
(i) 'A' shows the rate at which reaction decreases due to denaturation of enzyme molecules.
(ii) 'B' shows the rate at which reaction increases due to decreased kinetic energy of the substrate.
(iii) As temperature rises, more and more enzyme molecules are denatured and 'A' appears to fall.
(iv) 'B' shows the rate at which reaction increases due to increased kinetic energy of the substrate and enzyme molecules.
Refer to the given graph showing the state of ionisation of Zwitterion.
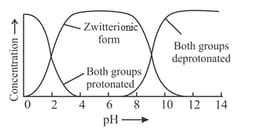
Select the correct statements regarding Zwitterion.
(i) Zwitterions can be formed from compounds that contain both acid groups and basic groups in their molecules.
(ii) A zwitterion can act either as proton donor or proton acceptor.
(iii) A monoamine monocarboxylic-amino acid is acid at high as both the groups (amino and carboxyl) lose a proton.
(iv) Amino acids in solution at neutral pH exist predominantly as dipolar ions, the amino group is protonated and the carboxyl group is deprotonated
Study the given data and answer the following question.
A sample of an enzyme called lactase was isolated from the intestinal lining of a calf. Assays were undertaken to evaluate the activity of the enzyme sample. The substrate of lactase is the disaccharide lactose. Lactase breaks a lactose molecule in two, producing a glucose molecule and a galactose molecule.
Two assays were carried out.
Assay 1:
| Lactose concentration (% w/v) | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Concentration of enzyme sample (% v/v) | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 |
| Reaction rate glucose sec-1 mL-1 | 0 | 25 | 50 | 75 | 100 | 125 |
Assay 2:
| Lactose concentration (% w/v) | 0 | 5 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 |
| Concentration of enzyme sample (% v/v) | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Reaction rate glucose sec-1 mL-1 | 0 | 15 | 25 | 35 | 40 | 40 |
What are the variables in each of the two assays?
Study the given data and answer the following question.
A sample of an enzyme called lactase was isolated from the intestinal lining of a calf. Assays were undertaken to evaluate the activity of the enzyme sample. The substrate of lactase is the disaccharide lactose. Lactase breaks a lactose molecule in two, producing a glucose molecule and a galactose molecule.
Two assays were carried out.
Assay 1:
| Lactose concentration (% w/v) | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Concentration of enzyme sample (% v/v) | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 |
| Reaction rate glucose sec-1 mL-1 | 0 | 25 | 50 | 75 | 100 | 125 |
Assay 2:
| Lactose concentration (% w/v) | 0 | 5 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 |
| Concentration of enzyme sample (% v/v) | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Reaction rate glucose sec-1 mL-1 | 0 | 15 | 25 | 35 | 40 | 40 |
Which of the following statements can be concluded from the two assays?
Choose a correct answer from the following.
