The theory of electrolytic dissociation suggests that:
The electrolyte on dissolution in water split up in two types of charged particles, i.e., cation and anions.
Important Questions on Electrochemistry
The electronic conductivity does not depend on
(where the constant B is positive)
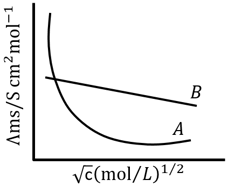
Following figure shows dependence of molar conductance of two electrolytes on concentration. is the limiting molar conductivity.
The number of Incorrect statement(s) from the following is _____
(A) for electrolyte is obtained by extrapolation
(B) For electrolyte graph is a straight line with intercept equal to
(C) At infinite dilution, the value of degree of dissociation approach zero for electrolyte .
(D) for any electrolyte or can be calculated using for individual ions.
Calculate the degree of dissociation of acetic acid, if its molar conductivity is .
Given: and .
Given,
of
of
of
All above measurements are done in an electrolytic cell. Assuming to be a strong electrolyte which of the following is/are incorrect?
Represent the union of two sets by Venn diagram for each of the following.
is a prime number between and
is an odd number between and
Write down the changes that will be seen, explain the reason behind when dilute was taken in an electrolytic cell and electric current was passed through it.
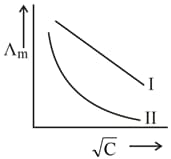
Above plot represents the variation of molar conductivity against (where, molar concentration of the electrolyte). Select the incorrect options among the following.