EASY
Earn 100
The value of for one mole of an ideal gas is nearly equal to
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Thermal Properties of Matter
EASY
An ideal gas equation can be written as, where and are respectively,
MEDIUM
One mole of an ideal gas passes through a process where pressure and volume obey the relation . Here and are constants. Calculate the change in the temperature of the gas if its volume changes from to .
EASY
A cylinder contains hydrogen gas at pressure of and temperature . Its density is:
HARD
Tyre of a bicycle has volume . Initially the tube is filled of its volume by air at atmospheric pressure . When a rider is on the bicycle, the area of contact of tyre with road is . The mass of rider with bicycle is . If a pump delivers a volume of air in each stroke then the number of strokes required to inflate the tyre is
EASY
The temperature of an open room of volume increases from to due to the sunshine. The atmospheric pressure in the room remains . If and are the number of molecules in the room before and after heating, then will be:
EASY
If a kilo mole of methane gas weighs , the density of methane at and pressure is (Use )
MEDIUM
The equation of state for of oxygen at a pressure and temperature , when occupying a volume will be
EASY
Two non-reactive monatomic ideal gases have their atomic masses in the ratio . The ratio of their partial pressures, when enclosed in a vessel kept at a constant temperature is . The ratio of their densities is
HARD
Two non-reactive monoatomic ideal gases have their atomic masses in the ratio 2 : 3. The ratio of their partial pressures, when enclosed in a vessel kept at a constant temperature, is 4 : 3. The ratio of their densities is
EASY
For the diagram given for an ideal gas
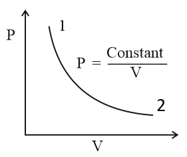
Out of the following which one correctly represents the diagram?
HARD
A container in the shape of a rectangular parallelepiped of length is divided internally by a movable partition as shown in the figure.
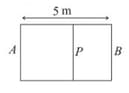
The left compartment is filled with a given mass of an ideal gas of molar mass while the right compartment is filled with an equal mass of another ideal gas of molar mass at same temperature. What will be the distance of from the left wall when equilibrium is established?
EASY
If pressure and temperature of an ideal gas are doubled and volume is halved, the number of molecules of gas
HARD
moles of an ideal diatomic gas with initial temperature is compressed from to . The thermodynamic process is such that , where is a constant. Then, the value of is close to (the gas constant, ).
EASY
Two vessels separately contain two ideal gases and at the same temperature. The pressure of gas is three times the pressure of gas . Under these conditions, the density of gas is found to be two times the density of . The ratio of molecular weights of gas and i.e. is
MEDIUM
Different curves in the figure show the behaviour of gases
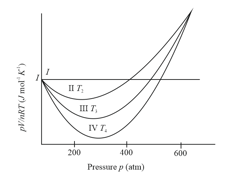
(i) Curve I represent ideal gas behaviour
(ii) Curves II, III and IV also represents ideal gas behaviour at different temperatures and
(iii) Curves II, III and IV represents behaviour of a real gas at different temperatures and
(iv)
(v)
The correct statements are
EASY
Two gases having same pressure and volume are mixed at a temperature . If the mixture is at a temperature and occupies the same volume then pressure of the mixture would be
EASY
For Boyle's law to hold good the necessary condition is
HARD
An open glass tube is immersed in mercury in such a way that a length of extends above the mercury level. The open end of the tube is then closed and sealed and the tube is raised vertically up by additional . What will be length of the air column above mercury in the tube now ?
(Atmospheric pressure = of Hg)
EASY
A given sample of an ideal gas occupies a volume, at a pressure, and absolute temperature, . The mass of each molecule of the gas is . Which of the following gives the density of the gas?
MEDIUM
A vertical closed cylinder is separated into two parts by a frictionless piston of mass and of negligible thickness. The piston is free to move along the length of the cylinder. The length of the cylinder above piston is and that below the piston is such that Each part of the cylinder contains moles of an ideal gas at equal temperature If the piston is stationary, its mass will be given by:
( is universal gas constant and is the acceleration due to gravity)

