The vapour pressure of two pure liquids, and , that form an ideal solution are and torr, respectively, at temperature . A mixture of the vapour of and for which the amount fraction of is is slowly compressed at temperature . Calculate:
(a) The composition of the first drop of the condensate,
(b) The total pressure when this drop is formed,
(c) The composition of the solution whose normal boiling point is .
(d) The pressure when only the last bubble of vapour remains.
(e) The composition of the last bubble.

Important Questions on States of Matter: Gases and Liquids
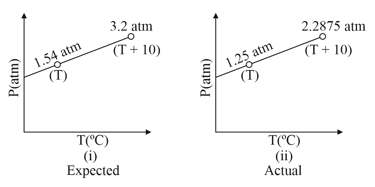
A closed vessel of known volume containing known amount of ideal gaseous substance 'A' was observed for variation of pressure with temperature. The expected graph was to be like as in
(i) However actual observations revealed the graph to be like.
(ii) The deviation was attributed to polymerisation of gas molecules an If it is known that the above reaction given only yield.
(a) Calculate the ratio of (where Total no. of gaseous mole actually present
Total no. of mole original taken)
(b) Find the value of to which the gas is being polymerised into
A water gas mixture has the composition by volume of and
(i) Calculate the volume in litres at STP of the mixture which on treatment with excess steam will contain litres of The stoichiometry for the water gas shift reaction is
(ii) Find the density of the water gas mixture in
(iii) Calculate the moles of the absorbants and ethanolamine.
required respectively to collect the gas obtained.
A gas present in a container connected to frictionless, weightless piston operating always at one atmosphere pressure such that it permits flow of gas outside (with no adding of gas). The graph of vs (Kelvin) was plotted & was found to be a straight line with co-ordinates of extremen points as Calculate :
(i) relationship between &
(ii) relationship between
(iii) Maxima or minima value of
